Page 65 - AN-1-2
P. 65
Advanced Neurology NMDA receptors in neuropsychiatric diseases
the two potentiators. The GEN-8324 has an impact on essential for the harmful effects of Aβ. Synaptic loss [212] ,
the inhibitory neurons only, while the GEN-6901 plays a impairment of LTP [212-214] , and increased LTD induced by
[38]
role in both inhibitory and excitatory neurons ; however, Aβ [215] can all be rescued by GluN2B antagonists. Some of
the underlying principle remaining to be explored. The these mechanisms may be the activation of extrasynaptic
GEN-0723 had been shown to enhance GluN2A not only GluN2B receptors induced by changes in glutamate
in vitro but also in vivo . The GEN-9278 potentiated uptake [215] . Phosphorylation of the GluN2B by the tau and
[39]
not only the GluN2A-NMDARs but also the GluN2B-, tyrosine protein kinase FYN trafficking to the dendritic
GluN2C- and GluN2D-NMDARs [210] . The GEN-9278 spine enhances the interaction with PSD95, which leads to
increased the glutamate and glycine potency and reduced downstream excitatory toxicity [216] . Besides, the induction
the deactivation of glutamate. of Aβ is needed for the activation of extrasynaptic
GluN2B-containing NMDARs [217] . A synthetic peptide that
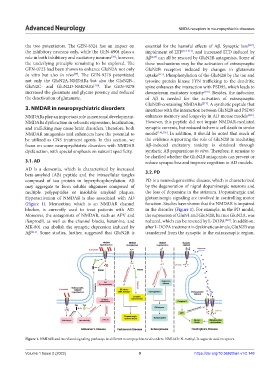
3. NMDAR in neuropsychiatric disorders interferes with the interaction between GluN2B and PSD95
NMDARs play an important role in neuronal development. enhances memory and longevity in AD mouse models [216] .
NMDARs dysfunction in subunits expression, localization, However, this peptide did not impair NMDAR-mediated
and trafficking may cause brain disorders. Therefore, both synaptic currents, but reduced ischemic cell death in stroke
NMDAR antagonists and enhancers have the potential to model [216,218] . In addition, it should be noted that much of
be utilized as CNS treatment agents. In this section, we the evidence supporting the role of GluN2B in mediating
focus on some neuropsychiatric disorders with NMDAR Aβ-induced excitatory toxicity is obtained through
dysfunction, with special emphasis on subunit specificity. synthetic Aβ preparations in vitro. Therefore, it remains to
be clarified whether the GluN2B antagonists can prevent or
3.1. AD reduce synapse loss and improve cognition in AD models.
AD is a dementia, which is characterized by increased 3.2. PD
beta-amyloid (Aβ) peptide and the intracellular tangles
composed of tau protein in hyperphosphorylation. Aβ PD is a neurodegenerative disease, which is characterized
may aggregate to form soluble oligomers composed of by the degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurons and
multiple polypeptides or insoluble amyloid plaques. the loss of dopamine in the striatum. Dopaminergic and
Hyperactivation of NMDAR is also associated with AD glutaminergic signaling are involved in controlling motor
(Figure 1). Memantine, which is an NMDAR channel function. Studies have shown that the NMDAR is impaired
blocker, is currently used to treat patients with AD. in the disorder (Figure 1). For example, in the PD model,
Moreover, the antagonists of NMDAR, such as APV and the expression of GluN1 and GluN2B, but not GluN2A, was
ifenprodil, as well as the channel blocks, ketamine, and reduced, which can be rescued by L-DOPA [219] . In addition,
MK-801 can abolish the synaptic depression induced by after L-DOPA treatment in dyskinetic animals, GluN2B was
Aβ [211] . Some studies, further, suggested that GluN2B is transferred from the synaptic to the extrasynaptic region,
Figure 1. NMDAR and its related signaling pathways in different neuropsychiatric disorders. NMDAR: N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v1i2.148