Page 74 - AN-3-1
P. 74
Advanced Neurology COVID-19 and neurodegenerative diseases
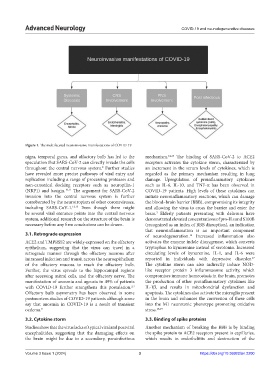
Figure 1. The multifaceted neuroinvasive manifestations of COVID-19
nigra, temporal gyrus, and olfactory bulb has led to the mechanism. 14,15 The binding of SARS-CoV-2 to ACE2
speculation that SARS-CoV-2 can directly invade the cells receptors activates the cytokine storm, characterized by
throughout the central nervous system. Further studies an increment in the serum levels of cytokines, which is
2
have revealed more precise pathways of viral entry and regarded as the primary mechanism resulting in lung
replication including a range of processing proteases and damage. Upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines
non-canonical docking receptors such as neuropilin-1 such as IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α has been observed in
(NRP1) and basigin. 10,11 The argument for SARS-CoV-2 COVID-19 patients. High levels of these cytokines can
invasion into the central nervous system is further initiate neuroinflammatory reactions, which can damage
corroborated by the neurotropism of other coronaviruses, the blood–brain barrier (BBB), compromising its integrity
including SARS-CoV-1. 12,13 Even though there might and allowing the virus to cross the barrier and enter the
be several viral entrance points into the central nervous brain. Elderly patients presenting with delirium have
3
system, additional research on the structure of the brain is demonstrated elevated concentrations of pro-ILs and S100B
necessary before any firm conclusions can be drawn. (recognized as an index of BBB disruption), an indication
that neuroinflammation is an important component
3.1. Retrograde expression of neurodegeneration. Increased inflammation also
16
ACE2 and TMPRSS2 are widely expressed on the olfactory activates the enzyme indole dioxygenase, which converts
epithelium, suggesting that the virus can travel in a tryptophan to kynurenine instead of serotonin. Increased
retrograde manner through the olfactory neurons after circulating levels of kynurenine, IL-1, and IL-6 were
17
intranasal infection and transit across the neuroepithelium reported in individuals with depressive disorder.
of the olfactory mucosa to reach the olfactory bulb. The cytokine storm can also indirectly induce NOD-
Further, the virus spreads to the hippocampal regions like receptor protein 3 inflammasome activity, which
after accessing mitral cells, and the olfactory nerve. The compromises immune homeostasis in the brain, promotes
manifestation of anosmia and ageusia in 49% of patients the production of other proinflammatory cytokines like
with COVID-19 further strengthens this postulation. IL-1β, and results in mitochondrial dysfunction and
2,3
Olfactory bulb asymmetry has been observed in some apoptosis. The cytokines also activate the microglia present
postmortem studies of COVID-19 patients although some in the brain and enhances the conversion of these cells
say that anosmia in COVID-19 is a result of transient into the M1 neurotoxic phenotype promoting oxidative
oedema. 3 stress. 18,19
3.2. Cytokine storm 3.3. Binding of spike proteins
Studies show that the virus lacks of typical viral and postviral Another mechanism of breaking the BBB is by binding
encephalitides, suggesting that the damaging effects on the spike protein to ACE2 receptors present in capillaries,
the brain might be due to a secondary, parainfectious which results in endotheliitis and destruction of the
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.2200