Page 25 - ARNM-1-2
P. 25
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine FAP-targeted RLT in cancer
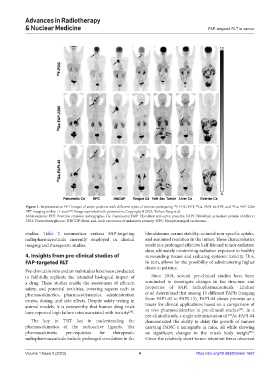
Figure 1. Representative PET images of seven patients with different types of tumors undergoing F-FDG PET, Ga-FAPI-46 PET, and Ga-FAP-2286
18
68
68
PET imaging within <1 week . Image reprinted with permission, Copyright © 2023, Yizhen Pang et al.
[28]
Abbreviations: PET: Positron emission tomography; Ca: Carcinoma; FAP: Fibroblast activation proteins; FAPI: Fibroblast activation protein inhibitor;
FDG: Fluorodeoxyglucose; HNCUP: Head-and-neck carcinoma of unknown primary; NPC: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
studies. Table 2 summarizes various FAP-targeting bloodstream, serum stability, reduced non-specific uptake,
radiopharmaceuticals currently employed in clinical and sustained retention in the tumor. These characteristics
imaging and therapeutic studies. result in a prolonged effective half-life and tumor radiation
dose, ultimately minimizing radiation exposure to healthy
4. Insights from pre-clinical studies of surrounding tissues and reducing systemic toxicity. This,
FAP-targeted RLT in turn, allows for the possibility of administering higher
doses to patients.
Pre-clinical in vitro and animal studies have been conducted
to faithfully replicate the intended biological impact of Since 2018, several pre-clinical studies have been
a drug. These studies enable the assessment of efficacy, conducted to investigate changes in the structure and
safety, and potential toxicities, covering aspects such as properties of FAPI radiopharmaceuticals. Lindner
pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, administration et al. determined that among 15 different FAPIs (ranging
routes, dosing, and side effects. Despite safety testing in from FAPI-02 to FAPI-15), FAPI-04 shows promise as a
animal models, it is noteworthy that human drug trials tracer for clinical applications based on a comparison of
[11]
have reported high failure rates associated with toxicity . in vivo pharmacokinetics in pre-clinical studies . In a
[29]
pre-clinical study, a single administration of Ac-FAPI-04
225
The key to TRT lies in understanding the demonstrated the ability to delay the growth of tumors
pharmacokinetics of the radioactive ligands. The carrying PANC-1 xenografts in mice, all while showing
pharmacokinetic pre-requisites for therapeutic no significant changes in the mice’s body weight .
[30]
radiopharmaceuticals include prolonged circulation in the Given the relatively short tumor retention times observed
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/arnm.1667