Page 46 - BH-2-4
P. 46
Brain & Heart Transforming transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis
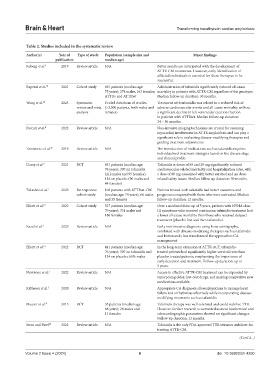
Table 2. Studies included in the systematic review
Author(s) Year of Type of study Population (sample size and Major findings
publication median age)
Ruberg et al. 9 2019 Review article N/A Better results are anticipated with the development of
ATTR-CM treatments. However, early identification of
afflicted individuals is essential for these therapies to be
successful.
Rapezzi et al. 19 2021 Cohort study 437 patients (median age: Administration of tafamidis significantly reduced all-cause
75 years); 274 males, 163 females; mortality in patients with ATTR-CM regardless of the genotype.
ATTRv and ATTRwt Median follow-up duration: 30 months.
Wang et al. 10 2023 Systematic Pooled data from 16 studies Treatment with tafamidis was related to a reduced risk of
review and meta- (>2,000 patients, both males and adverse cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality without
analysis females) a significant decline in left ventricular ejection fraction
in patients with ATTRwt. Median follow-up duration:
24 – 30 months.
Porcari et al. 8 2022 Review article N/A Non-invasive imaging techniques are crucial for assessing
myocardial involvement in ATTR amyloidosis and can play a
significant role in evaluating disease-modifying therapies and
guiding treatment adjustments.
Yamamoto et al. 20 2019 Review article N/A The introduction of medications such as tafamidis requires
individualized treatment strategies based on the disease stage
and clinical profile.
Damy et al. 4 2021 RCT 441 patients (median age: Tafamidis at doses of 80 and 20 mg significantly reduced
76 years); 307 on tafamidis cardiovascular-related mortality and hospitalization rates, with
(212 males and 95 females), a dose of 80 mg associated with better survival and no dose-
134 on placebo (90 males and related safety issues. Median follow-up duration: 30 months.
44 females)
Takashio et al. 7 2023 Retrospective 103 patients with ATTRwt-CM Patients treated with tafamidis had better outcomes and
cohort study (median age: 78 years); 68 males prognoses compared with those who were untreated. Median
and 35 females follow-up duration: 12 months.
Elliott et al. 13 2023 Cohort study 517 patients (median age: Over a median follow-up of 5 years, patients with NYHA class
79 years); 331 males and III symptoms who received continuous tafamidis treatment had
186 females a lower all-cause mortality than those who received delayed
treatment (placebo first and then tafamidis).
Raval et al. 2 2023 Review article N/A Early non-invasive diagnosis using bone scintigraphy,
combined with disease-modifying therapies such as tafamidis
and bortezomib, has transformed the approach to CA
management.
Elliott et al. 11 2022 RCT 441 patients (median age: In the long-term extension of ATTR-ACT, tafamidis-
76 years); 307 on tafamidis and treated patients had significantly higher survival rates than
134 on placebo; 68% males placebo-treated patients, emphasizing the importance of
early detection and treatment. Follow-up duration: up to
5 years.
Nuvolone et al. 5 2022 Review article N/A Access to effective ATTR-CM treatment can be expanded by
repurposing older, low-cost drugs, and making competitive new
medications available.
Kittleson et al. 3 2020 Review article N/A Appropriate CA diagnosis allows physicians to manage heart
failure and arrhythmias effectively while incorporating disease-
modifying treatments such as tafamidis.
Maurer et al. 21 2015 RCT 35 patients (median age: Tafamidis therapy was well-tolerated and could stabilize TTR.
68 years); 24 males and However, further research is warranted as most biochemical and
11 females echocardiographic parameters showed no significant changes.
Follow-up duration: 12 months.
Stern and Patel 22 2022 Review article N/A Tafamidis is the only FDA-approved TTR tetramer stabilizer for
treating ATTR-CM.
(Cont'd...)
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2024) 6 doi: 10.36922/bh.4250