Page 298 - EJMO-9-3
P. 298
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Helicobacter pylori infection and Alzheimer’s disease
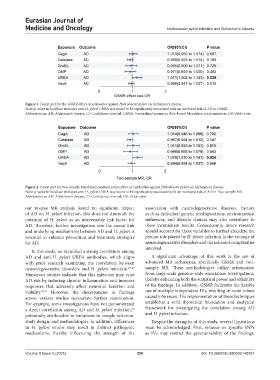
Figure 1. Forest plot for the GSMR effect of antibodies against Helicobacter pylori on Alzheimer’s disease
Note: p-value in boldface indicates anti-H. pylori UREA was found to be significantly associated with an increased risk of AD in GSMR.
Abbreviations: AD: Alzheimer’s disease; CI: Confidence interval; GSMR: Generalized summary data–based Mendelian randomization; OR: Odds ratio.
Figure 2. Forest plot for two-sample Mendelian randomization effect of antibodies against Helicobacter pylori on Alzheimer’s disease
Note: p-value in boldface indicates anti-H. pylori UREA was found to be significantly associated with an increased risk of AD in Two-sample MR.
Abbreviations: AD: Alzheimer’s disease; CI: Confidence interval; OR: Odds ratio.
our reverse MR analysis found no significant impact association with neurodegenerative diseases. Factors
of AD on H. pylori infection, this does not diminish the such as individual genetic predispositions, environmental
potential of H. pylori as an intervenable risk factor for influences, and lifestyle choices may also contribute to
AD. Therefore, further investigation into the causal link these inconsistent results. Consequently, future research
and underlying mechanisms between AD and H. pylori is should account for these variables to further elucidate the
essential to enhance prevention and treatment strategies precise role played by H. pylori infection in the etiology of
for AD. neurodegenerative disorders and the inherent complexities
involved.
In this study, we identified a strong correlation among
AD and anti-H. pylori UREA antibodies, which aligns A significant advantage of this work is the use of
with prior research examining the correlation between advanced MR techniques, specifically GSMR and two-
neurodegenerative disorders and H. pylori infection. 27-29 sample MR. These methodologies utilize information
Numerous studies indicate that this infection may raise from large-scale genome-wide association investigations,
AD risk by inducing chronic inflammation and immune thereby enhancing both the statistical power and reliability
responses that adversely affect neuronal function and of the findings. In addition, GSMR facilitates the flexible
viability. 30,31 However, the discrepancies in findings use of multiple independent IVs, resulting in more robust
across various studies necessitate further examination. causal inferences. The implementation of these techniques
For example, some investigations have not demonstrated establishes a solid theoretical foundation and analytical
a direct correlation among AD and H. pylori infection, framework for investigating the correlation among AD
32
potentially attributable to variations in sample selection, and H. pylori infection.
study design, and methodologies. In addition, differences Despite the strengths of this study, several limitations
in H. pylori strains may result in distinct pathogenic must be acknowledged. First, reliance on specific SNPs
mechanisms, thereby influencing the strength of the as IVs may restrict the generalizability of the findings.
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2025) 290 doi: 10.36922/EJMO025140087