Page 11 - GHES-3-2
P. 11
Global Health Economics and
Sustainability
Flow states in neurodivergence: Cognitive integration
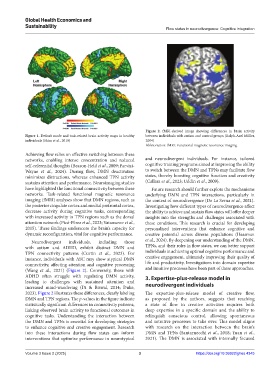
Figure 2. fMRI-derived image showing differences in brain activity
Figure 1. Default mode and task-related brain activity maps in healthy between individuals with autism and control groups (Ralph-Axel Müller,
individuals (Shim et al., 2010) 2004)
Abbreviation: fMRI: Functional magnetic resonance imaging.
Achieving flow relies on effective switching between these
networks, enabling intense concentration and reduced and neurodivergent individuals. For instance, tailored
self-referential thoughts (Beason-Held et al., 2009; Parvizi- cognitive training programs aimed at improving the ability
Wayne et al., 2024). During flow, DMN deactivation to switch between the DMN and TPNs may facilitate flow
minimizes distractions, whereas enhanced TPN activity states, thereby boosting cognitive function and creativity
sustains attention and performance. Neuroimaging studies (Callara et al., 2023; Uddin et al., 2009).
have highlighted the functional connectivity between these Future research should further explore the mechanisms
networks. Task-related functional magnetic resonance underlying DMN and TPN interactions, particularly in
imaging (fMRI) analyses show that DMN regions, such as the context of neurodivergence (De La Serna et al., 2021).
the posterior cingulate cortex and medial prefrontal cortex, Investigating how different types of neurodivergence affect
decrease activity during cognitive tasks, corresponding the ability to achieve and sustain flow states will offer deeper
with increased activity in TPN regions such as the dorsal insights into the strengths and challenges associated with
attention network (Picó-Pérez et al., 2023; Vatansever et al., these conditions. This research is crucial for developing
2015). These findings underscore the brain’s capacity for personalized interventions that enhance cognitive and
dynamic reconfiguration, vital for cognitive performance. creative potential across diverse populations (Heasman
Neurodivergent individuals, including those et al., 2024). By deepening our understanding of the DMN,
with autism and ADHD, exhibit distinct DMN and TPNs, and their roles in flow states, we can better support
TPN connectivity patterns (Curtin et al., 2023). For individuals in achieving optimal cognitive performance and
instance, individuals with ASC may show atypical DMN creative engagement, ultimately improving their quality of
connectivity, affecting attention and cognitive processing life and productivity. Investigations into domain expertise
(Wang et al., 2021) (Figure 2). Conversely, those with and intuitive processes have been part of these approaches.
ADHD often struggle with regulating DMN activity, 3. Expertise-plus-release model in
leading to challenges with sustained attention and neurodivergent individuals
increased mind-wandering (Di & Biswal, 2014; Duke,
2023). Figure 2 illustrates these differences, clearly labeling The expertise-plus-release model of creative flow,
DMN and TPN regions. The p-values in the figure indicate as proposed by the authors, suggests that reaching
statistically significant differences in connectivity patterns, a state of flow in creative activities requires both
linking observed brain activity to functional outcomes in deep expertise in a specific domain and the ability to
cognitive tasks. Understanding the interaction between relinquish conscious control, allowing spontaneous
the DMN and TPNs is essential for developing strategies and intuitive processes to take over. This model aligns
to enhance cognitive and creative engagement. Research with research on the interaction between the brain’s
into these interactions during flow states can inform DMN and TPNs (Santarnecchi et al., 2018; Yuan et al.,
interventions that optimize performance in neurotypical 2021). The DMN is associated with internally focused
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2025) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.4345