Page 31 - GPD-2-1
P. 31
Gene & Protein in Disease Therapeutic opportunities in hydrogen sulfide for cancer research
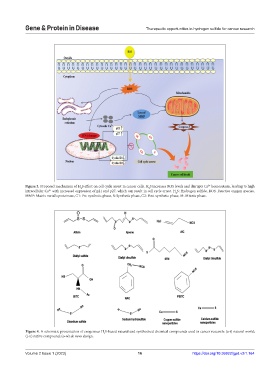
Figure 3. Proposed mechanism of H S effect on cell cycle arrest in cancer cells. H S increases ROS levels and disrupts Ca homeostasis, leading to high
2+
2
2
intracellular Ca with increased expression of p21 and p27, which can result in cell cycle arrest. H S: Hydrogen sulfide, ROS: Reactive oxygen species,
2+
2
MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase, G1: Pre-synthetic phase, S: Synthetic phase, G2: Post-synthetic phase, M: Mitotic phase.
Figure 4. A schematic presentation of exogenous H S-based natural and synthesized chemical compounds used in cancer research: (a-i) natural world;
2
(j-n) native compound; (o-w) de novo design.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 16 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.v2i1.164