Page 52 - GPD-3-4
P. 52
Gene & Protein in Disease Immune checkpoint blocker and NK cell activation
region of BCMA with the extracellular domain of MICA,
has shown significant potential for NK cell activation in
BCMA-positive multiple myeloma cells both in vivo and
in vitro through NK cell degranulation. 100
Given that cancer cells can evade and develop resistance
to single therapeutic approaches, combination therapies
targeting multiple sites may provide enhanced treatment
outcomes. Previous research has suggested that antibodies
targeting tumor-derived soluble NKG2D ligand sMIC
can reprogram NK cell homeostasis and enhance PD-L1
blockade therapy in melanoma patients by upregulating
CD25 expression on NK cells. In addition, ICB-resistant
101
patients have been shown to have higher NKG2D-L
expression in cancer cell surfaces, making them more
susceptible to NKG2DL-mediated treatments. Moreover,
102
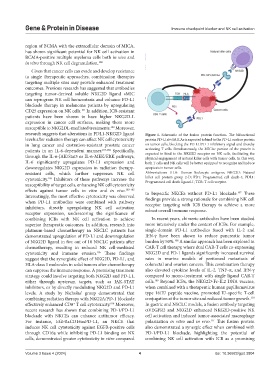
research suggests that alterations in PDL1-NKG2D ligand Figure 1. Schematic of the fusion protein function. The bifunctional
levels after radiation therapy can affect NK cell cytotoxicity protein PD-L1sFv/MICAe is expected to bind to the PD-L1 surface protein
in lung cancer and castration-resistant prostate cancer on tumor cells, blocking the PD-L1/PD-1 inhibitory signal and thereby
patients in an IL-6-dependent manner. 103,104 Specifically, activating T cells. Simultaneously, the MICAe portion of the protein is
expected to bind to the NKG2D receptor on NK cells, facilitating the
through the IL-6-JAK/Stat3 or IL-6-MEK/ERK pathways, physical engagement of natural killer cells with tumor cells. In this way,
IL-6 significantly upregulates PD-L1 expression and both T cells and NK cells will be better equipped to recognize and induce
downregulates NKG2D expression in radiation therapy- apoptosis in tumor cells.
resistant cells, which further suppresses NK cell Abbreviations: HLA: Human leukocyte antigens; NKG2D: Natural
cytotoxicity. Inhibitors of these pathways increase the killer cell protein group 2-D; PD1: Programmed cell death-1; PDL1:
105
Programmed cell death ligand-1; TCR: T cell receptor.
susceptibility of target cells, enhancing NK cell cytotoxicity
effects against tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. 103-105 to bispecific NKCEs without PD-L1 blockade. These
107
Interestingly, the most effective cytotoxicity was observed findings provide a strong rationale for combining NK cell
when PD-L1 antibodies were combined with pathway
inhibitors, directly upregulating NK cell activation receptor targeting with ICB therapy to achieve a more
robust overall immune response.
receptor expression, underscoring the significance of
combining ICBs with NK cell activation to achieve In recent years, chimeric antibodies have been studied
superior therapeutic outcomes. In addition, research into more intensively under the context of ICBs. For example,
platinum-based chemotherapy in NSCLC patients has single-domain PD-L1 antibodies fused with IL-2 and
demonstrated upregulation of PD-L1 and downregulation IFN-γ have been shown to reduce pancreatic tumor
of NKG2D ligand in five out of 10 NSCLC patients after burden by 50%. A similar approach has been explored in
108
chemotherapy, resulting in reduced NK cell-mediated CAR-T cell therapy, where dual CAR-T cells co-expressing
cytotoxicity and immune evasion. These findings NKG2D and PD-1 ligands significantly increased survival
105
suggest that the synergistic effect of NKG2D, PD-L1, and rates in murine models of peritoneal metastasis of
HLA-class 1 molecules in solid tumors after chemotherapy colorectal and ovarian cancers. This combination therapy
can suppress the immune response. A promising treatment also elevated cytokine levels of IL-2, TNF-α, and IFN-γ
strategy could involve targeting both NKG2D and PD-L1, compared to mono-treatment with single ligand CAR-T
109
either through upstream targets, such as JAK-STAT cells. Beyond ICBs, the NKG2D-Fc-IL2 DNA vaccine,
inhibitors, or by directly modulating NKG2D and PD-L1 when combined with a therapeutic human papillomavirus
levels. A study by Nicholas’ group demonstrated that type 16/E7 peptide vaccine, promoted E7-specific T-cell
combining radiation therapy with NKG2A/PD-1 blockade conjugation at the tumor site and reduced tumor growth.
110
effectively enhanced CD8 T cell cytotoxicity. Moreover, In gastric and NSCLC models, a fusion antibody targeting
106
+
recent research has shown that combining PD-1/PD-L1 αVEGFR2 and NKG2D enhanced NKG2D-positive NK
blockade with NKCEs can enhance antitumor efficacy. cell activation and induced tumor-associated macrophage
111
For instance, EGFRxCD16axPD-L1, an NKCE that polarization in vitro and in vivo. This fusion protein
induces NK cell cytotoxicity against EGFR-positive cells also demonstrated a synergic effect when combined with
through CD16a while inhibiting PD-L1 binding on NK PD-1/PD-L1 blockade, highlighting the potential of
cells, demonstrated greater cytotoxicity in vitro compared combining NK cell activation with ICB as a promising
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/gpd.3804