Page 35 - GPD-4-1
P. 35
Gene & Protein in Disease GPER1 in brain and heart diseases
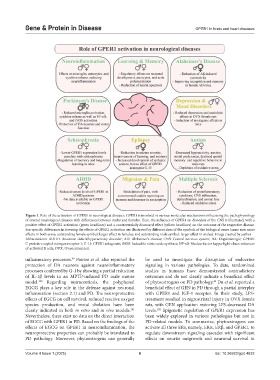
Figure 1. Role of the activation of GPER1 in neurological diseases. GPER1 is involved in various molecular mechanisms influencing the pathophysiology
of several neurological diseases with differences between males and females. Here, the influence of GPER1 on disorders of the CNS is illustrated, with a
positive effect of GPER1 activation (green headlines) and a controversially discussed effect (yellow headlines) on the outcome of the respective disease.
Sex-specific differences in favoring the effects of GPER1 activation are illustrated by different sizes of the symbols of the biological sexes (same size: same
effects in both sexes; outstanding female symbol: larger effect in females; and outstanding male symbol: larger effect in males). Image created by author
Abbreviations: ADHD: Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; AD: Alzheimer’s disease; CNS: Central nervous system; DA: Dopaminergic; GPER1:
G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1; G-15: GPER1 antagonist; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer
of activated B cells; OVX: Ovariectomized.
inflammatory processes. Poirier et al. also reported the be used to investigate the disruption of endocrine
99
protection of DA neurons against neuroinflammatory signaling in various pathologies. To date, randomized
processes conferred by G-1 by showing a partial reduction studies in humans have demonstrated contradictory
of IL-1β levels in an MPTP-induced PD male mouse outcomes and do not clearly indicate a beneficial effect
model. Regarding nutraceuticals, the polyphenol of phytoestrogens on PD pathology. Du et al. reported a
100
43
EGCG plays a key role in the defense against neuronal beneficial effect of GEN in PD through a partial interplay
inflammation (section 2.1) and PD. The neuroprotective with GPER1 and IGF-1 receptor. In their study, LPS-
effects of EGCG on cell survival, reduced reactive oxygen treatment resulted in nigrostriatal injury in OVX female
species production, and metal chelation have been rats, with GEN application restoring LPS-decreased DA
clearly indicated in both in vitro and in vivo models. levels. Epigenetic regulation of GPER1 expression has
102
101
Nevertheless, there exist no data on the direct interaction been widely explored in various pathologies but not in
of EGCG with GPER1 in PD. Based on the findings of the PD-related models. To summarize, phytoestrogens can
effects of EGCG on GPER1 in neuroinflammation, the activate all three ERs, namely, ERα, ERβ, and GPER1, to
neuroprotective properties can probably be translated to regulate downstream signaling cascades with significant
PD pathology. Moreover, phytoestrogens can generally effects on neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival in
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4632