Page 97 - GTM-2-1
P. 97
Global Translational Medicine Resveratrol’s EC barrier protection is dependent on KLF2
A B
C
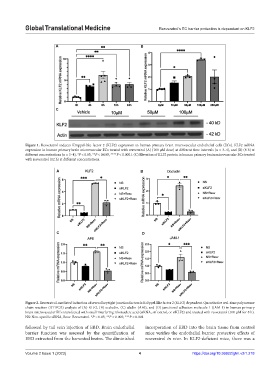
Figure 1. Resveratrol induces Krϋppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) expression in human primary brain microvascular endothelial cells (ECs). KLF2 mRNA
expression in human primary brain microvascular ECs treated with resveratrol (A) (100 µM dose) at different time intervals (n = 3–4), and (B) (8 h) at
different concentrations (n = 3–4), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ****P < 0.0001. (C) Elevation of KLF2 protein in human primary brain microvascular ECs treated
with resveratrol (12 h) at different concentrations.
A B
C D
Figure 2. Resveratrol-mediated induction of several key tight junction factors is Krϋppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) dependent. Quantitative real-time polymerase
chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis of (A) KLF2, (B) occludin, (C) afadin (AF6), and (D) junctional adhesion molecule 1 (JAM-1) in human primary
brain microvascular ECs transfected with small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA, siControl, or siKLF2) and treated with resveratrol (100 μM for 8 h).
NS: Non-specific siRNA, Resv: Resveratrol. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005; ***P < 0.001.
followed by tail vein injection of EBD. Brain endothelial incorporation of EBD into the brain tissue from control
barrier function was assessed by the quantification of mice verifies the endothelial barrier protective effects of
EBD extracted from the harvested brains. The diminished resveratrol in vivo. In KLF2-deficient mice, there was a
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v2i1.218