Page 22 - GTM-4-3
P. 22
Global Translational Medicine Anti-inflammatory therapy in CVD
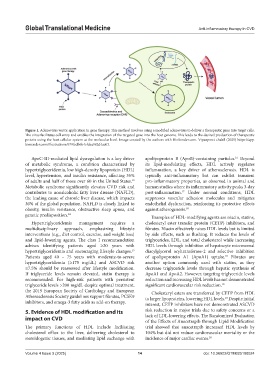
Figure 1. Adenovirus vector application in gene therapy. This method involves using a modified adenovirus to deliver a therapeutic gene into target cells.
The virus facilitates cell entry and enables the integration of the targeted gene into the host genome. This leads to the desired production of therapeutic
protein using the host cellular system at the molecular level. Image created by the authors with BioRender.com. Vipanpreet chahil (2025) https://app.
biorender.com/illustrations/679fedb6b4efdea982d4ae03.
ApoC-III-mediated lipid dysregulation is a key driver apolipoprotein B (ApoB)-containing particles. Beyond
16
of metabolic syndrome, a condition characterized by its lipid-modulating effects, HDL actively regulates
hypertriglyceridemia, low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) inflammation, a key driver of atherosclerosis. HDL is
level, hypertension, and insulin resistance, affecting 35% typically anti-inflammatory but can exhibit transient
of adults and half of those over 60 in the United States. pro-inflammatory properties, as observed in animal and
13
Metabolic syndrome significantly elevates CVD risk and human studies where its inflammatory activity peaks 3-day
contributes to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), post-inflammation. Under normal conditions, HDL
17
the leading cause of chronic liver disease, which impacts suppresses vascular adhesion molecules and mitigates
30% of the global population. NAFLD is closely linked to endothelial dysfunction, reinforcing its protective effects
obesity, insulin resistance, obstructive sleep apnea, and against atherogenesis. 18
genetic predisposition. 14 Examples of HDL-modifying agents are niacin, statins,
Hypertriglyceridemia management requires a cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitors, and
multidisciplinary approach, emphasizing lifestyle fibrates. Niacin effectively raises HDL levels but is limited
interventions (e.g., diet control, exercise, and weight loss) by side effects, such as flushing. It reduces the levels of
and lipid-lowering agents. The class I recommendation triglycerides, LDL, and total cholesterol while increasing
advises identifying patients aged ≥20 years with HDL levels through inhibition of hepatocyte microsomal
hypertriglyceridemia and encouraging lifestyle changes. diacylglycerol acyltransferase-2 and selective inhibition
15
Patients aged 40 – 75 years with moderate-to-severe of apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1) uptake. Fibrates are
18
hypertriglyceridemia (≥175 mg/dL) and ASCVD risk another option commonly used with statins, as they
≥7.5% should be reassessed after lifestyle modification. decrease triglyceride levels through hepatic synthesis of
If triglyceride levels remain elevated, statin therapy is ApoA1 and ApoA2. However, targeting triglyceride levels
recommended. For high-risk patients with persistent reduction and increasing HDL levels has not demonstrated
triglyceride levels >200 mg/dL despite optimal treatment, significant cardiovascular risk reduction. 18
the 2019 European Society of Cardiology and European Cholesteryl esters are transferred by CETP from HDL
Atherosclerosis Society guidelines support fibrates, PCSK9 to larger lipoproteins, lowering HDL levels. Despite initial
18
inhibitors, and omega-3 fatty acids as add-on therapy. interest, CETP inhibitors have not demonstrated ASCVD
5. Evidence of HDL modification and its risk reduction in major trials due to safety concerns or a
impact on CVD lack of LDL-lowering effects. The Randomized Evaluation
of the Effects of Anacetrapib through Lipid Modification
The primary functions of HDL include facilitating trial showed that anacetrapib increased HDL levels by
cholesterol efflux to the liver, delivering cholesterol to 104% but did not reduce cardiovascular mortality or the
steroidogenic tissues, and mediating lipid exchange with incidence of major cardiac events. 18
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 14 doi: 10.36922/GTM025100024