Page 51 - IJPS-11-3
P. 51
International Journal of
Population Studies Early marriage and birth in Bengali women
Table 1. Socioeconomic and demographic profiles of the age of 18. Nearly one-third had experienced both early
married women aged 15 – 49, 2019 – 2021 marriage and childbearing. Among the sample, 55% were
native Bengali speakers whereas the remaining spoke
Background characteristics Percentage Total other languages. Over one-fifth (21%) of the women were
women (N)
Age at marriage illiterate, and a quarter had completed 10 or more years of
schooling. Approximately one-third of the women had no
<18 years 46.2 23,604 exposure to mass media. Most women (86%) lived in male-
18 years and above 53.8 27,465 headed households. Of the sample, 67% identified as Hindu,
Married before 18 & childbearing with the remainder identifying as non-Hindus. In terms of
before 19 years social group, 47% of the women were non-SC/ST/OBC,
No 66.3 33,850 20% were SC, 12% were ST, and 20% were OBC. Regarding
Yes 33.7 17,219 economic status, 34% of the women belonged to the
Native language poorest category, 31% were poorer, 19% were in the middle
Non-Bengali 45.4 23,185 category, 11% were richer, and 5% belonged to the richest
category. A majority (78%) of the women resided in rural
Bengali 54.6 27,883 areas. With respect to the states, a substantial percentage of
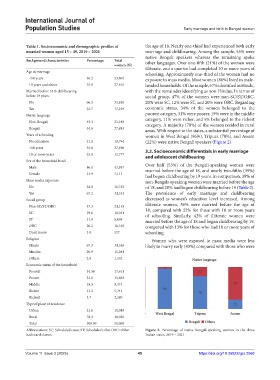
Years of schooling women in West Bengal (96%), Tripura (78%), and Assam
No education 21.1 10,794 (22%) were native Bengali speakers (Figure 2).
<10 years 53.8 27,498 3.2. Socioeconomic differentials in early marriage
10 or more years 25.0 12,777 and adolescent childbearing
Sex of the household head
Male 86.1 43,957 Over half (53%) of the Bengali-speaking women were
married before the age of 18, and nearly two-fifths (39%)
Female 13.9 7,111 had begun childbearing by 19 years. In comparison, 39% of
Mass media exposure non-Bengali-speaking women were married before the age
No 32.8 16,735 of 18, and 28% had begun childbearing before 19 (Table 2).
Yes 67.2 34,334 The prevalence of early marriage and childbearing
Social group decreased as women’s education level increased. Among
Non-SC/ST/OBC 47.3 24,135 illiterate women, 56% were married before the age of
SC 19.6 10,031 18, compared with 22% for those with 10 or more years
of schooling. Similarly, 42% of illiterate women were
ST 11.9 6,058 married before the age of 18 and began childbearing by 19,
OBC 20.2 10,318 compared with 13% for those who had 10 or more years of
Don’t know 1.0 527 schooling.
Religion Women who were exposed to mass media were less
Hindu 67.3 34,356 likely to marry early (43%) compared with those who were
Muslim 29.9 15,281
Others 2.8 1,432
Economic status of the household
Poorest 34.58 17,611
Poorer 31.1 15,864
Middle 18.5 9,473
Richer 11.2 5,741
Richest 4.7 2,380
Type of place of residence
Urban 21.6 11,049
Rural 78.4 40,020
Total 100.00 51,069
Abbreviations: SC: Scheduled caste; ST: Scheduled tribe; OBC: Other Figure 2. Percentage of native Bengali-speaking women in the three
backward classes. Indian states, 2019 – 2021
Volume 11 Issue 3 (2025) 45 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.2068