Page 83 - IJPS-11-3
P. 83
International Journal of
Population Studies Low fertility intentions in China
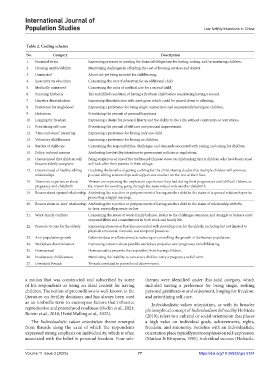
Table 2. Coding scheme
No. Category Description
1. Financial strain Expressing pressure in meeting the financial obligations for having, raising, and/or nurturing children.
2. Housing unaffordability Mentioning challenges in affording the cost of housing services and shelter.
3. Unmarried About not yet being married for childbearing.
4. Insecurity on education Concerning the cost of education for an additional child.
5. Medically uninsured Concerning the costs of medical care for a second child.
6. Pursuing firstborn The unfulfilled condition of having a firstborn child before considering having a second.
7. Genetics dissatisfaction Expressing dissatisfaction with one’s gene, which could be passed down to offspring.
8. Preference for singlehood Expressing a preference for being single, unmarried, and consequently having no children.
9. Hedonism Prioritizing the pursuit of personal happiness.
10. Longing for freedom Expressing a desire for personal liberty and the ability to live a life without constraints or restrictions.
11. Prioritizing self-care Prioritizing the pursuit of self-care and personal improvement.
12. “One-and-done” parenting Expressing a preference for having only one child.
13. Voluntary childlessness Expressing a preference for having no children.
14. Burden of childcare Concerning the responsibilities, challenges, and demands associated with raising and caring for children.
15. Policy-induced reasons Attributing low fertility intentions to government policies or regulations.
16. Unconvinced that children will Being suspicious of one of the traditional Chinese views on childrearing that is children who have been raised
become elderly caregivers will look after their parents in their old age.
17. Unconvinced of healthy sibling Doubting the benefits of getting a sibling for the child. Having doubts that multiple children will promote
relationships positive sibling relationships and support one another for the rest of their lives.
18. Traumatic experiences about Women are expressing the unpleasant experiences they had during their pregnancies and (difficult) labors, as
pregnancy and childbirth the reason for avoiding going through the same ordeal with another childbirth.
19. Reason about spousal relationship Attributing the rejection or postponement of having another child to the status of a spousal relationship or to
preserving a happy marriage.
20. Reason about in-laws’ relationship Attributing the rejection or postponement of having another child to the status of relationship with the
in-laws, especially parents-in-law.
21. Work-family conflicts Concerning the issues of work-family balance. Refers to the challenges, tensions, and struggle to balance one’s
responsibilities and commitments in both work and family life.
22. Pressure to care for the elderly Expressing stressors or burdens associated with providing care for the elderly, including but not limited to
physical, emotional, financial, and temporal pressures.
23. Anti-population growth Refers to ideas or efforts aimed at reducing or controlling the growth of the human population.
24. Workplace discrimination Expressing concern about possible workplace prejudice over pregnancy and childcaring.
25. Homosexual Homosexuality prevents the respondent from having children.
26. Involuntary childlessness Mentioning the inability to conceive a child or carry a pregnancy to full term.
27. Unrelated threads Threads unrelated to parenthood determinants.
a notion that was constructed and subscribed by some themes were identified under this axial category, which
of his respondents as being an ideal context for having included having a preference for being single, seeking
children. The notion of preconditions is well-known in the personal gratification and enjoyment, longing for freedom,
literature on fertility decisions and has always been used and prioritizing self-care.
as an umbrella term to encompass factors that influence Individualistic values orientation, as with its broader
reproductive and parenthood readiness (Bodin et al., 2021; philosophical concept of Individualism defined by Hofstede
Boivin et al., 2018; Hviid Malling et al., 2022). (2010), refers to a cultural or social orientation that places
The Individualistic values orientation theme emerged a high value on individual goals, achievements, rights,
from threads along the axial of which the respondents freedom, and autonomy. Societies with an individualistic
expressed strong emphasis on individuality, which is often orientation place typically more emphasis on self-expression
associated with the belief in personal freedom. Four sub- (Markus & Kitayama, 1991), individual success (Hofstede,
Volume 11 Issue 3 (2025) 77 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.5124