Page 14 - IJPS-8-1
P. 14
International Journal of
Population Studies Validity and reliability of Mini-Mental State Examination in older Chinese
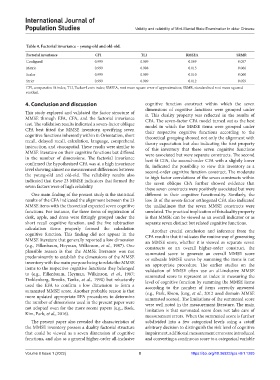
Table 4. Factorial invariance – young‑old and old‑old.
Factorial invariance CFI TLI RMSEA SRMR
Configural 0.999 0.999 0.009 0.057
Metric 0.999 0.998 0.015 0.066
Scalar 0.999 0.999 0.010 0.060
Strict 0.999 0.999 0.012 0.059
CFI, comparative fit index; TLI, Tucker-Lewis index; RMSEA, root mean square error of approximation; SRMR, standardized root mean squared
residual.
4. Conclusion and discussion cognitive function construct within which the seven
dimensions of cognitive functions were grouped under
This study explored and validated the factor structure of it. This duality property was reflected in the results of
MMSE through EFA, CFA, and the factorial invariance CFA. The seven-factor CFA model turned out as the best
test. The validation results indicated a seven-factor oblique model in which the MMSE items were grouped under
CFA best fitted the MMSE inventory, specifying seven their respective cognitive functions according to the
cognitive functions inherently within it: Orientation, short theoretical grouping showed not only the alignment with
recall, delayed recall, calculation, language, comprehend theory expectation but also indicating the first property
instruction, and visuospatial. These results were similar to of this inventory that these seven cognitive functions
MMSE literature on their cognitive functions but differed were associated but were separate constructs. The second
in the number of dimensions. The factorial invariance best fit CFA, the second-order CFA with a slightly lower
confirmed the hypothesized CFA was at a high invariance fit, indicated the possibility to view this inventory as a
level showing almost no measurement differences between second-order cognitive function construct. The moderate
the young-old and old-old. The reliability results also to high factor correlations of the seven constructs within
indicated that these 23 MMSE indicators that formed the the seven oblique CFA further showed evidence that
seven factors were of high reliability.
these seven constructs were positively associated but were
One main finding of the present study is the statistical different in their cognitive functionality. Similarly, the
results of the CFA indicated the alignment between the 23 low fit of the seven-factor orthogonal CFA also indicated
MMSE items with the theoretical expected seven cognitive the unlikeliness that the seven MMSE constructs were
functions. For instance, the three items of registration of unrelated. The practical implication of this duality property
desk, apple, and dress were fittingly grouped under the is that MMSE can be viewed as an overall indicator or as
short recall cognitive function, and the five subtraction separate seven distinct but related cognitive functions.
calculation items properly formed the calculation Another crucial conclusion and inference from the
cognitive function. This finding did not appear in the CFA result is that it indicates the routine way of generating
MMSE literature that generally reported a low dimension an MMSE score, whether it is viewed as separate seven
(e.g., Fillenbaum, Heyman, Wilkinson, et al., 1987). One constructs or an overall higher-order construct, the
plausible reason is that the MMSE literature was not summated score to generate an overall MMSE score
predominantly to establish the dimensions of the MMSE or subscale MMSE scores by summing the items is not
inventory with the main purpose being to relate the MMSE an appropriate procedure. The earlier studies on the
items to the respective cognitive functions they belonged validation of MMSE often use an all-inclusive MMSE
to (e.g., Fillenbaum, Heyman, Wilkinson, et al., 1987; summated score to represent an index in measuring the
Tinklenberg, Brooks, Tanke, et al., 1990) but reluctantly level of cognitive function by summing the MMSE items
used the EFA to confirm a low dimension to form a according to the number of items correctly answered
summated MMSE score. Another probable reason is that (e.g., Park, Kwon, Jung, et al., 2012 used domain MMSE
more updated appropriate EFA procedures to determine summated scores). The limitations of the summated score
the number of dimensions used in the present paper were were well noted in the measurement literature. The main
not adopted even for the more recent papers (e.g., Baek, limitation is that summated score does not take care of
Kim, Park, et al., 2016). measurement errors. When the summated score is further
The present paper also revealed the characteristics of subdivided into a few categorical levels using a cutoff
the MMSE inventory possess a duality factorial structure arbitrary decision to distinguish the risk level of cognitive
that could be viewed as a seven dimension of cognitive impairment, additional measurement errors are introduced
functions, and also as a general higher-order all-inclusive and converting a continuous score to a categorical variable
Volume 8 Issue 1 (2022) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.v8i1.1285