Page 100 - ITPS-7-2
P. 100
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences ABT for NDO
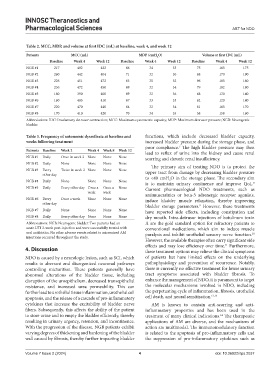
Table 2. MCC, MDP, and volume at first IDC (mL) at baseline, week 4, and week 12
Patients MCC (mL) MDP (cmH O) Volume at first IDC (mL)
2
Baseline Week 4 Week 12 Baseline Week 4 Week 12 Baseline Week 4 Week 12
NGB #1 217 402 422 66 34 33 75 165 175
NGB #2 260 442 404 71 32 30 88 170 190
NGB #3 226 451 472 63 35 32 96 185 180
NGB #4 236 472 450 69 32 34 79 182 180
NGB #5 180 390 400 69 32 36 68 130 140
NGB #6 160 405 410 67 33 33 62 120 140
NGB #7 220 470 440 64 32 34 81 165 170
NGB #8 170 410 420 70 34 35 58 158 160
Abbreviations: IDC: Involuntary detrusor contraction; MCC: Maximum cystometric capacity; MDP: Maximum detrusor pressure; NGB: Neurogenic
bladder.
Table 3. Frequency of autonomic dysreflexia at baseline and functions, which include decreased bladder capacity,
weeks following treatment increased bladder pressure during the storage phase, and
poor compliance. The high bladder pressure may then
7
Patients Baseline Week 2 Week 4 Week 8 Week 12 lead to reflux of urine into the kidney and cause renal
NGB #1 Daily Once in week 2 None None None scarring and chronic renal insufficiency.
NGB #2 Daily None None None None The primary aim of treating NDO is to protect the
NGB #3 Every Twice in week 2 None None None upper tract from damage by decreasing bladder pressure
other day
2
NGB #4 Daily None None None None to <40 cmH O in the storage phase. The secondary aim
is to maintain urinary continence and improve QoL.
8
NGB #5 Daily Every other day Once a Once a None Current pharmacological NDO treatments, such as
week week antimuscarinics or beta-3 adrenergic receptor agonists,
NGB #6 Every Once a week None None None induce bladder muscle relaxation, thereby improving
other day bladder storage parameters. However, these treatments
9
NGB #7 Daily None None None None have reported side effects, including constipation and
NGB #8 Daily Every other day None None None dry mouth. Intra-detrusor injections of botulinum toxin
Abbreviations: NGB: Neurogenic bladder. Two patients had an A are the gold standard option for refractory patients to
acute UTI 2-week post-injection and were successfully treated with conventional medications, which aim to induce muscle
oral antibiotics. No other adverse events related to micronized AM paralysis and inhibit urothelial sensory nerve function.
10
injections occurred throughout the study.
However, the available therapies often carry significant side
effects and may lose efficiency over time. Furthermore,
11
4. Discussion these treatment options may relieve the clinical symptoms
NDO is caused by a neurologic lesion, such as SCI, which of patients but have limited effects on the underlying
results in aberrant and disorganized neuronal pathways pathophysiology and prevention of recurrence. Notably,
controlling micturition. These patients generally have there is currently no effective treatment for lower urinary
abnormal alterations of the bladder tissue, including tract symptoms associated with bladder fibrosis. To
disruption of the uroepithelium, decreased transepithelial enhance the management of NDO, it is paramount to target
resistance, and increased urea permeability. This can the molecular mechanisms involved in NDO, including
further lead to urothelial tissue inflammation, urothelial cell the perpetuating cycle of inflammation, fibrosis, urothelial
apoptosis, and the release of a cascade of pro-inflammatory cell death, and neural sensitization. 12,13
cytokines that increase the excitability of bladder nerve AM is known to contain anti-scarring and anti-
fibers. Subsequently, this affects the ability of the patient inflammatory properties and has been used in the
to store urine and to empty the bladder efficiently, thereby treatment of many clinical indications. The therapeutic
14
resulting in urinary urgency, retention, and incontinence. applications of AM are diverse, and the mechanisms of
With the progression of the disease, NGB patients exhibit action are multimodal. The immunomodulatory function
varying degrees of thickening and hardening of the bladder is related to the apoptosis of pro-inflammatory cells and
wall caused by fibrosis, thereby further impacting bladder the suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as
Volume 7 Issue 2 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/itps.2037