Page 13 - ITPS-7-2
P. 13
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Novel pharmacologic therapies for SAH
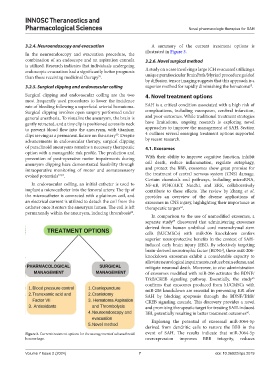
3.2.4. Neuroendoscopy and evacuation A summary of the current treatment options is
In the neuroendoscopy and evacuation procedure, the illustrated in Figure 3.
combination of an endoscope and an aspiration cannula 3.2.6. Novel surgical method
is utilized. Research indicates that individuals undergoing
endoscopic evacuation had a significantly better prognosis A study on a case involving a large ICH evacuated utilizing a
59
than those receiving medicinal therapy . unique parafascicular BrainPath/Myriad procedure guided
by diffusion tensor imaging suggests that this approach is a
63
3.2.5. Surgical clipping and endovascular coiling superior method for rapidly diminishing the hematoma .
Surgical clipping and endovascular coiling are the two 4. Novel treatment options
most frequently used procedures to lower the incidence
rate of bleeding following a superficial arterial hematoma. SAH is a critical condition associated with a high risk of
Surgical clipping involves open surgery performed under complications, including vasospasm, cerebral infarction,
general anesthesia. To visualize the aneurysm, the brain is and poor outcomes. While traditional treatment strategies
gently retracted, and a tiny clip is positioned across its neck have limitations, ongoing research is exploring novel
to prevent blood flow into the aneurysm, with titanium approaches to improve the management of SAH. Section
clips serving as a permanent fixture on the artery . Despite 4 outlines several emerging treatment options supported
60
advancements in endovascular therapy, surgical clipping by recent research.
of paraclinoid aneurysms remains a necessary therapeutic 4.1. Exosomes
option with a manageable risk profile. The prediction and
prevention of post-operative motor impairments during With their ability to improve cognitive function, inhibit
aneurysm clipping have demonstrated feasibility through cell death, reduce inflammation, regulate autophagy,
intraoperative monitoring of motor and somatosensory and protect the BBB, exosomes show great promise for
evoked potentials 61,62 . the treatment of central nervous system (CNS) damage.
Certain chemicals and pathways, including microRNA,
In endovascular coiling, an initial catheter is used to NF-κB, PI3K/AKT, Notch1, and ERK, collaboratively
implant a microcatheter into the femoral artery. The tip of contribute to these effects. The review by Zhang et al.
the microcatheter is connected with a platinum coil, and provides an overview of the diverse applications of
an electrical current is utilized to detach the coil from the exosomes in CNS injury, highlighting their importance as
catheter once it enters the aneurysm lumen. The coil is left therapeutic targets .
64
permanently within the aneurysm, inducing thrombosis .
60
In comparison to the use of unmodified exosomes, a
separate study discovered that administering exosomes
65
derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem
cells (hUCMSCs) with miR-206 knockdown confers
superior neuroprotective benefits in the context of SAH-
induced early brain injury (EBI). By selectively targeting
brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), these miR-206-
knockdown exosomes exhibit a considerable capacity to
alleviate neurological impairments, reduce brain edema, and
mitigate neuronal death. Moreover, in vivo administration
of exosomes modified with miR-206 activates the BDNF/
TrkB/CREB signaling pathway. Essentially, the study
65
confirms that exosomes produced from hUCMSCs with
miR-206 knockdown are essential in preventing EBI after
SAH by blocking apoptosis through the BDNF/TrkB/
CREB signaling cascade. This discovery provides a novel
and promising therapeutic target for treating SAH-induced
EBI, potentially resulting in better treatment outcomes .
66
Exploring the potential of exosomal miR-3064-5p
derived from dendritic cells to restore the BBB in the
Figure 3. Current treatment options for the management of subarachnoid event of SAH. The results indicate that miR-3064-5p
hemorrhage. overexpression improves BBB integrity, reduces
Volume 7 Issue 2 (2024) 7 doi: 10.36922/itps.2019