Page 106 - ITPS-7-3
P. 106
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Alpha-2A receptor agonist and addiction
lower intrinsic efficacy than [Met ]enkephalin and 7. Conclusion
5
[D-Ala , MePhe , Gly -ol]enkephalin. This adaptation
4
5
2
was not attributed to any changes in the properties of the To assist the readership’s comprehension, a summary
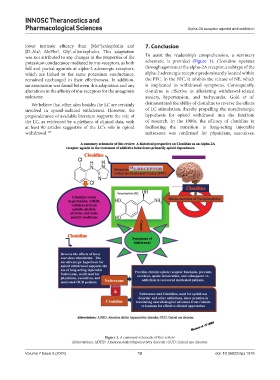
potassium conductance mediated by mu-receptors, as both schematic is provided (Figure 1). Clonidine operates
full and partial agonists at alpha-2 adrenergic receptors, through agonism at the alpha-2A receptor, a subtype of the
which are linked to the same potassium conductance, alpha-2 adrenergic receptor predominantly located within
remained unchanged in their effectiveness. In addition, the PFC. In the PFC, it inhibits the release of NE, which
no association was found between this adaptation and any is implicated in withdrawal symptoms. Consequently,
alterations in the affinity of mu-receptors for the antagonist clonidine is effective in alleviating withdrawal-related
naloxone. anxiety, hypertension, and tachycardia. Gold et al.
We believe that other sites besides the LC are certainly demonstrated the ability of clonidine to reverse the effects
involved in opioid-induced withdrawal. However, the of LC stimulation, thereby propelling the noradrenergic
preponderance of available literature supports the role of hypothesis for opioid withdrawal into the forefront
the LC, as evidenced by a plethora of clinical data, with of research. In the 1980s, the efficacy of clonidine in
at least 80 articles suggestive of the LC’s role in opioid facilitating the transition to long-acting injectable
withdrawal. 175 naltrexone was confirmed for physicians, executives,
Figure 1. A summary schematic of this review
Abbreviations: ADHD: Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; OUD: Opioid use disorder.
Volume 7 Issue 3 (2024) 12 doi: 10.36922/itps.1918