Page 78 - ITPS-8-2
P. 78
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Ketamine and SOD activity in schizophrenia
Table 1. Locomotor activity assessment
S/N Treatments Movement counts/5 min Numbers of rearing
in activity cage (secs)
1. VEH 377.4±14.6** 9±0.71**
2. KET 549.0±19.9 16.40±0.93
3. KET+RISP 446.0±10.2** 10.40±0.93**
Notes: Ketamine-induced hyperactivity (spontaneous movement and
rearing events) in mice.
Values represent mean±S.E.M of 5 animals per group. In one-way
analysis of variance test (ANOVA), (F .000, 9.552] = 31.43, P<0.0001;
[2
F .000, 11. = 20.88, P<0.0001), VEH and KET+RISP groups showed
40
[2
significant difference when compared with KET group. **P<0.05 as
compared with KET group.
Abbreviations: VEH: Vehicle; KET: Ketamine; RISP: Risperidone.
Table 2. Evaluation of anxiety‑induced poor exploratory
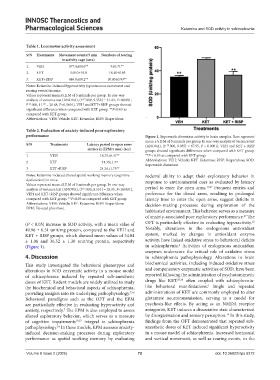
performance Figure 1. Superoxide dismutase activity in brain samples. Bars represent
mean ± S.E.M of 5 animals per group. In one-way analysis of variance test
S/N Treatments Latency period in open arms (ANOVA), (F .000, 9.055] = 67.55, P < 0.0001), VEH and KET + RISP
[2
entries in EPM/5 min) (sec) groups showed significant differences when compared with KET group.
1 VEH 18.79±0.47** **P < 0.05 as compared with KET group.
2 KET 34.30±1.77 Abbreviations: VEH: Vehicle; KET: Ketamine; RISP: Risperidone; SOD:
Superoxide dismutase.
3 KET+RISP 24.36±1.75**
Notes: Ketamine-induced altered spatial working memory (cognitive rodents’ ability to adapt their exploratory behavior in
dysfunction) in mice. response to environmental cues as evaluated by latency
Values represent mean±S.E.M of 5 animals per group. In one-way 13,27
analysis of variance test (ANOVA), (F .000, 8.551] = 28.95, P<0.0001), period to enter the open arms. Frequent entries and
[2
VEH and KET+RISP groups showed significant difference when preference for the closed arms, resulting in prolonged
compared with KET group. **P<0.05 as compared with KET group. latency time to enter the open arms, suggest deficits in
Abbreviations: VEH: Vehicle; KET: Ketamine; RISP: Risperidone; decision-making processes during exploration of the
EPM: Elevated plus maze.
habituated environment. This behavior serves as a measure
of anxiety-associated poor exploratory performance. The
27
12
(P < 0.05) increase in SOD activity, with a mean value of OFT is particularly effective in evaluating hyperactivity.
49.98 ± 0.51 unit/mg protein, compared to the VEH and Notably, alterations in the endogenous antioxidant
KET + RISP groups, which showed mean values of 34.84 system, marked by changes in antioxidant enzyme
± 1.06 and 36.52 ± 1.30 unit/mg protein, respectively activity, have linked oxidative stress to behavioral deficits
2
(Figure 1). in schizophrenia. Activities of endogenous antioxidant
enzymes underscore the critical role of oxidative stress
4. Discussion in schizophrenia pathophysiology. Alterations in brain
This study investigated the behavioral phenotypes and biochemical activities, including induced oxidative stress
alterations in SOD enzymatic activity in a mouse model and compensatory enzymatic activities of SOD, have been
of schizophrenia induced by repeated sub-anesthetic reported following the administration of psychotomimetic
doses of KET. Rodent models are widely utilized to study drugs like KET. 29,30 often coupled with schizophrenia-
6
the biochemical and behavioral aspects of schizophrenia, like behavioral manifestations. Single and repeated
providing insights into its underlying pathophysiology. administrations of KET are commonly employed to alter
7,16
Behavioral paradigms such as the OFT and the EPM glutamate neurotransmission, serving as a model for
are particularly effective in evaluating hyperactivity and psychosis-like effects. By acting as an NMDA receptor
anxiety, respectively. The EPM is also employed to assess antagonist, KET induces a dissociative state characterized
7
14
altered exploratory behavior, which serves as a measure by disorganization and sensory perception. In this study,
of cognitive impairments 13,27 integral to schizophrenia findings from the OFT demonstrated that repeated sub-
pathophysiology. In these models, EPM assesses anxiety- anesthetic doses of KET induced significant hyperactivity
16
induced decision-making processes during exploratory in a mouse model of schizophrenia. Increased horizontal
performance as spatial working memory by evaluating and vertical movement, as well as rearing events, in the
Volume 8 Issue 2 (2025) 72 doi: 10.36922/itps.6372