Page 30 - ITPS-8-3
P. 30
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Benzodiazepine use and retention in OAT
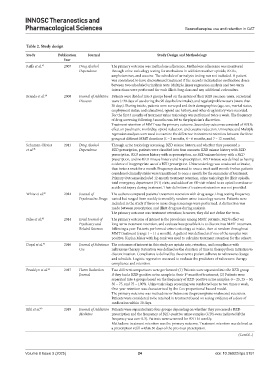
Table 2. Study design
Study Publication Journal Study Design and Methodology
Year
Raffa et al. 47 2007 Drug Alcohol The primary outcome was methadone adherence. Methadone adherence was monitored
Dependence through urine toxicology testing for methadone in addition to other opioids, BZDs,
amphetamines, and cocaine. The schedule of urinalysis testing was not included. A patient
was considered to have discontinued treatment if the records indicated no methadone doses
between two scheduled urinalysis tests. Multiple linear regression analysis and two-term
interactions were performed for each illicit drug class and any additional cofounders.
Brands et al. 40 2008 Journal of Addictive Patients were divided into 3 groups based on the nature of their BZD use: non-users, occasional
Diseases users (<30 days of use during the 90 days before intake), and regular/problem users (more than
30 days). During intake, patients were surveyed and their demographics (age, sex, marital status,
employment status, and education), opioid use history, and other drug history were recorded.
For the first 3 months of treatment urine toxicology was performed twice a week. The frequency
of drug screening following 3 months was left to the physician's discretion.
Treatment retention of MMT was the primary outcome. Secondary outcomes consisted of BZD’s
effect on psychiatric morbidity, opioid reduction, and cocaine reduction. Univariate and Multiple
regression analyses were used to examine the difference in treatment retention between the three
groups at different MMT durations (1 – 3 months, 4 – 6 months, and 7 – 12 months).
Schuman-Olivier 2013 Drug Alcohol Through urine toxicology screening, BZD misuse history, and whether they possessed a
et al. 45 Dependence BZD prescription, patients were classified into four consorts: BZD misuse history with BZD
prescription, BZD misuse history with no prescription, no BZD misuse history with a BZD
prescription, and no BZD misuse history and no prescription. BZD misuse was defined as having
evidence of inappropriate use of a BZD prescription. Urine toxicology was conducted at intake,
then twice a week for a month. Frequency decreased to once a week until month 6 when patients
considered clinically stable were transitioned to once a month for the remainder of treatment.
Primary Outcomes included 12-month treatment retention, urine toxicology for illicit opioids,
total emergency department (ED) visits, and odds of an ED visit related to an opioid overdose or
accidental injury during treatment. Their definition of treatment retention was not provided.
White et al. 48 2014 Journal of The authors compared patients' treatment retention with drug usage. Drug testing frequency
Psychoactive Drugs varied but ranged from weekly to monthly random urine toxicology screens. Patients were
included in the study if three or more drug screenings were performed. A distinction was
made between prescription and illicit drug use during analysis.
The primary outcome was treatment retention; however, they did not define the term.
Peles et al. 50 2014 Israel Journal of The primary outcome of interest is the prevalence among MMT patients, BZD’s effect on
Psychiatry and long-term treatment retention, and evaluate how possible it is to discontinue MMT treatment
Related Sciences following a year. Patients performed urine toxicology at intake, then at random throughout
MMT treatment (range 1 – 11 a month). A patient was defined as if one of the samples was
positive. Kaplan Meier with log-rank was used to calculate treatment retention for the cohort.
Dayal et al. 43 2016 Journal of Substance The outcomes of interest in this study are uptake rate, retention, and compliance with
Use naltrexone therapy. Retention was defined as the duration of time in therapy from initiation to
discontinuation. Compliance is defined by the extent a patient adheres to naltrexone dosage
and schedule. Logistic regression was used to evaluate the predictors of naltrexone therapy
compliance and retention.
Franklyn et al. 42 2017 Harm Reduction Two different comparisons were performed: (1) Patients were separated into the BZD group
Journal if they had a BZD-positive urine sample in their 1 month of treatment; (2) Patients were
st
separated into 4 groups based on the frequency of BZD-positive urine samples: 0 – 25, 25 – 50,
50 – 75, and 75 – 100%. Urine toxicology screening was conducted one to two times a week.
One-year retention was characterized by the Cox proportional hazard model.
The primary outcome was methadone or Suboxone (buprenorphine+naloxone) retention.
Patients were considered to be retained in treatment based on seeing evidence of a dose of
medication within 30 days.
Eibl et al. 49 2019 Journal of Addiction Patients were separated into four groups depending on whether they processed a BZD
Medicine prescription and the frequency of BZD-positive urine samples (UDS+was indicated if the
frequency was over 0.3). Patients were screened for BZD bi-weekly.
Methadone treatment retention was the primary outcome. Treatment retention was defined as
a prescription refill within 30 days of the previous prescription.
(Cont'd...)
Volume 8 Issue 3 (2025) 24 doi: 10.36922/itps.5151