Page 26 - JCAU-5-2
P. 26
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Style evolution rules of Tibetan dwellings
Third, the façade of most new dwellings is plastered proportion of wood veneers (more like the dwellings in
and decorated, and no longer pursues the expression the Tibetan Region in Jiarong (Editorial Committee of the
of traditional cultural elements in detail, leading to the Atlas of Tibetan Dwellings in Sichuan 2016)).
disappearance of artistic and cultural value. The doors
and windows are mostly replaced with modern materials 3.2. Proposal of dwellings’ prototype
for performance considerations, and the roofs are mostly Combining the preservation status and representativeness
replaced with new materials such as windowsills and of the dwellings studied, we selected four types of typical
colored steel plates for lower maintenance costs and
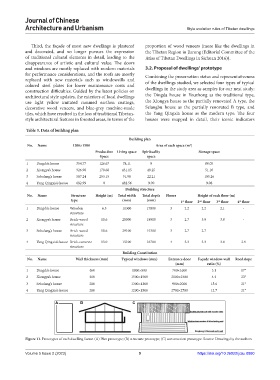
construction difficulties. Guided by the latest policies on dwellings in the study area as samples for our next study:
architectural style updates, the exteriors of local dwellings the Dingda house in Youzhong as the traditional type,
use light yellow imitated rammed earthen coatings, the Xiongya house as the partially renovated A type, the
decorative wood veneers, and blue-grey machine-made Selangbu house as the partially renovated B type, and
tiles, which have resulted in the loss of traditional Tibetan- the Yang Qingxia house as the modern type. The four
style architectural features in forested areas, in terms of the houses were mapped in detail, their iconic indicators
Table 3. Data of building plan
Building plan
No. Name 1200×1500 Area of each space (m )
2
Production Living space Spirituality Storage space
Space space
1 Dingda’s house 354.77 126.67 78.11 0 80.05
2 Xiongya’s house 926.98 170.68 431.15 48.25 51.10
3 Sebulang’s house 587.24 253.15 91.98 22.21 105.26
4 Yang Qingxia’s house 682.99 0 482.56 9.90 9.08
Building structure
No. Name Structure Height (m) Total width Total depth Floors Height of each floor (m)
type (mm) (mm) 1 floor 2 floor 3 floor 4 floor
rd
th
nd
st
1 Dingda’s house Wooden 6.5 11300 17000 3 2.2 2.2 2.1 -
structure
2 Xiongya’s house Brick-wood 10.6 28000 18000 3 2.7 3.0 3.0 -
structure
3 Sebulang’s house Brick-wood 10.6 29100 15300 3 2.7 2.7 - -
structure
4 Yang Qingxia’s house Brick-concrete 13.0 15100 16700 4 3.3 3.3 3.0 2.9
structure
Building Constitution
No. Name Wall thickness (mm) Typical windows (mm) Entrance door Façade window-wall Roof slope
(mm) ratio (%)
1 Dingda’s house 460 1000×800 700×1600 3.1 17°
2 Xiongya’s house 400 1500×1500 2100×2300 4.4 23°
3 Sebulang’s house 280 1300×1300 900×2000 15.6 21°
4 Yang Qingxia’s house 280 1200×1500 2700×2700 12.7 21°
A B C
Figure 11. Prototypes of each dwelling factor. (A) Plan prototype; (B) structure prototype; (C) construction prototype. Source: Drawings by the authors
Volume 5 Issue 2 (2023) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.0880