Page 72 - JCAU-5-2
P. 72
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Chinese troglodyte villages toward tourism
connected enhancement process as well. Thus, all (iv). Reuse: it refers to UBH elements that have been
typologies considered are expressions of the local and dismissed regarding their primary function but reused
national history and culture, potentially leading to both within another function.
heritage-led economic development and the straightening (v). Re-building: it refers to new cave elements built
of the places’ identity. following the historical techniques adopted for
This method has been utilized and refined during the construction of UBH, responding to the same
several ongoing projects; thus, some categories were functions as the new ones.
re-elaborated and/or modified concerning the already In China, interpretation, protection, abandonment,
published methodology. At this stage, the method provides reuse, and re-building were all adopted from case to case
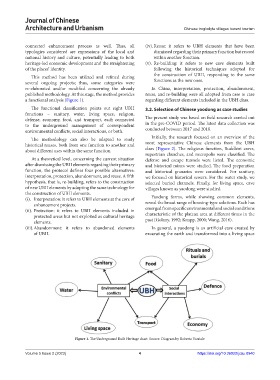
a functional analysis (Figure 1). regarding different elements included in the UBH class.
The functional classification points out eight UBH 3.2. Selection of Chinese yaodong as case studies
functions – sanitary, water, living space, religion,
defense, economy, food, and transport, each connected The present study was based on field research carried out
to the underground management of correspondent in the pre-COVID period. The latest data collection was
environmental conflicts, social interactions, or both. conducted between 2017 and 2018.
The methodology can also be adapted to study Initially, the research focused on an overview of the
historical reuses, both from one function to another and most representative Chinese elements from the UBH
about different uses within the same function. class (Figure 2). The religious function, Buddhist caves,
rupestrian churches, and necropolis were classified. The
At a theoretical level, concerning the current situation defense and escape tunnels were listed. The economic
after dismissing the UBH elements regarding their primary and historical mines were studied. The food preparation
function, the protocol defines four possible alternatives: and historical granaries were considered. For sanitary,
interpretation, protection, abandonment, and reuse. A fifth we focused on historical sewers. For the water study, we
hypothesis, that is, re-building, refers to the construction selected buried channels. Finally, for living space, cave
of new UBH elements by adopting the same technology for villages known as yaodong were studied.
the construction of UBH elements.
(i). Interpretation: it refers to UBH elements at the core of Yaodong forms, while showing common elements,
enhancement projects. reveal the broad range of housing-type solutions. Each has
(ii). Protection: it refers to UBH elements included in emerged from specific environmental and social conditions
protected areas but not exploited as cultural heritage characteristic of the plateau area at different times in the
elements. past (Golany, 1992; Knapp, 2000; Wang, 2016).
(iii). Abandonment: it refers to abandoned elements In general, a yaodong is an artificial cave created by
of UBH. excavating the earth and transformed into a living space
Figure 1. The Underground Built Heritage chart. Source: Diagram by Roberta Varriale
Volume 5 Issue 2 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.0940