Page 104 - JCAU-5-4
P. 104
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Cultural landscape in Huizhou City
Guangfu people reside in this cultural landscape area, and evolved from the three-room-and-two-corridor layout of
the interplay of these three folk cultures has resulted in the Guangfu area, Hakka-style row houses in some of the
various traditional village cultural landscapes. The cultural villages, and various architectural forms contribute to the
landscape area is interspersed with hills and plains, and the lack of uniformity in residential buildings across most of
rivers are dense, creating a landscape relationship near the the villages, often featuring a mix of style within a single
mountains and the water. The village buildings are densely village.
laid out along the terrain and rivers, featuring large-scale
structures at the core of the village landscape pattern. 3.3.5. Cultural landscape area of traditional villages
Farmland is distributed around the buildings according in eastern hilly area
to the water, and fishponds are constructed for fishery The Eastern Hilly Traditional Villages Cultural Landscape
culture near the sea. This gives rise to a landscape pattern Area mainly includes the area traversed by the Wuqiu
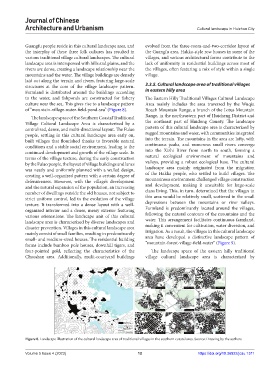
of “mountain-village-water-field-pond-sea” (Figure 8). Roach Mountain Range, a branch of the Lotus Mountain
The landscape space of the Southern Coastal Traditional Range, in the northeastern part of Huicheng District and
Village Cultural Landscape Area is characterized by a the northeast part of Huidong County. The landscape
centralized, dense, and multi-directional layout. The Fulao pattern of this cultural landscape area is characterized by
people, settling in this cultural landscape area early on, rugged mountains and water, with communities integrated
built villages that flourished thanks to favorable natural into the terrain. The mountains in the area are lofty, with
conditions and a stable social environment, leading to the continuous peaks, and numerous small rivers converge
continued development and growth of the village scale. In into the Xizhi River from north to south, forming a
terms of the village texture, during the early construction natural ecological environment of mountains and
by the Fulao people, the layout of village buildings and lanes valleys, providing a robust ecological base. The cultural
was neatly and uniformly planned with a walled design, landscape area mainly originated from the migration
creating a well-organized pattern with a certain degree of of the Hakka people, who settled to build villages. The
defensiveness. However, with the village’s development mountainous environment challenged village construction
and the natural expansion of the population, an increasing and development, making it unsuitable for large-scale
number of dwellings outside the old houses, not subject to clans living. This, in turn, determined that the villages in
strict uniform control, led to the evolution of the village this area would be relatively small, scattered in the small
texture. It transformed into a dense layout with a well- depressions between the mountains or river valleys.
organized interior and a dense, messy exterior featuring Farmland is predominantly located around the villages,
various orientations. The landscape unit of this cultural following the natural contours of the mountains and the
landscape area is characterized by diverse landscapes and water. This arrangement facilitates continuous farmland,
disaster prevention. Villages in this cultural landscape area making it convenient for cultivation, water diversion, and
mainly consist of small families, resulting in predominantly irrigation. As a result, the villages in this cultural landscape
small- and medium-sized houses. The residential building area have developed a distinctive landscape pattern of
forms include bamboo pole houses, downhill tigers, and “mountain-forest-village-field-water” (Figure 9).
four-pointed gold, reflecting the characteristics of the The landscape space of the eastern hilly traditional
Chaoshan area. Additionally, multi-courtyard buildings village cultural landscape area is characterized by
Figure 8. Landscape illustration of the cultural landscape area of traditional villages in the southern coastal area. Source: Drawing by the authors
Volume 5 Issue 4 (2023) 12 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.1311