Page 173 - JCAU-7-3
P. 173
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Urban orientalism and informal urbanization
rapid transformations have redefined the city’s skyline valuable insights into Jinan’s shifting urban layout. It
and urban structure, with tall buildings symbolizing also showcases local initiatives, such as urban renewal
vertical expansion and new residential developments and informal settlement regulation, aimed at fostering
marking outward growth. However, these changes have social cohesion and mitigating urban challenges. As
produced mixed outcomes. While economic growth Jinan continues its trajectory of growth, sustainability
and modernization have progressed, challenges such is expected to become a priority, focusing on energy
as environmental degradation, strained transportation efficiency, environmental protection, and inclusivity to
systems, and increased social inequality have emerged. achieve balanced and equitable urban development.
These dynamics underscore the pressing need for In summary, the growth of informal settlements and
sustainable and equitable urban planning approaches. urban changes in Jinan exemplifies the dynamic processes
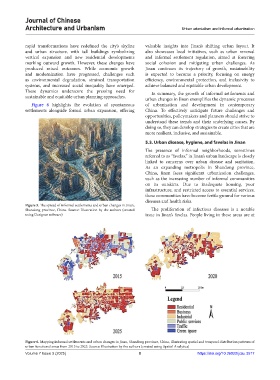
Figure 6 highlights the evolution of spontaneous of urbanization and development in contemporary
settlements alongside formal urban expansion, offering China. To effectively anticipate future challenges and
opportunities, policymakers and planners should strive to
understand these trends and their underlying causes. By
doing so, they can develop strategies to create cities that are
more resilient, inclusive, and sustainable.
5.3. Urban disease, hygiene, and favelas in Jinan
The presence of informal neighborhoods, sometimes
referred to as “favelas,” in Jinan’s urban landscape is closely
linked to concerns over urban disease and sanitation.
As an expanding metropolis in Shandong province,
China, Jinan faces significant urbanization challenges,
such as the increasing number of informal communities
on its outskirts. Due to inadequate housing, poor
infrastructure, and restricted access to essential services,
these communities have become fertile ground for various
diseases and health risks.
Figure 5. The spread of informal settlements and urban changes in Jinan,
Shandong province, China. Source: Illustration by the authors (created The proliferation of infectious diseases is a notable
using Designer software) issue in Jinan’s favelas. People living in these areas are at
Figure 6. Mapping informal settlements and urban changes in Jinan, Shandong province, China, illustrating spatial and temporal distribution patterns of
urban functional areas from 2015 to 2025. Source: Illustration by the authors (created using Spatial Analytics)
Volume 7 Issue 3 (2025) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.3517