Page 23 - JCAU-7-3
P. 23
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Natural ventilation in courtyard dwellings
intensity in complex courtyard airflow environments. different seasons and urban densities should be prioritized
Recent advances in hybrid modeling techniques, such as as essential directions for future research.
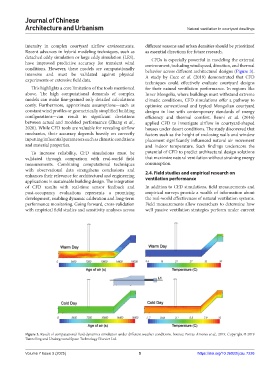
detached eddy simulation or large eddy simulation (LES), CFDs is especially powerful in modeling the external
have improved predictive accuracy for transient wind environment, including wind speed, direction, and thermal
conditions. However, these models are computationally behavior across different architectural designs (Figure 3).
intensive and must be validated against physical A study by Cuce et al. (2019) demonstrated that CFD
experiments or extensive field data.
techniques could effectively evaluate courtyard designs
This highlights a core limitation of the tools mentioned for their natural ventilation performance. In regions like
above. The high computational demands of complex Inner Mongolia, where buildings must withstand extreme
models can make fine-grained only detailed calculations climatic conditions, CFD simulations offer a pathway to
costly. Furthermore, approximate assumptions—such as optimize conventional and typical Mongolian courtyard
constant wind profiles or geometrically simplified building designs in line with contemporary standards of energy
configurations—can result in significant deviations efficiency and thermal comfort. Benni et al. (2016)
between actual and modeled performance (Zhang et al., applied CFD to investigate airflow in courtyard-shaped
2020). While CFD tools are valuable for revealing airflow houses under desert conditions. The study discovered that
mechanics, their accuracy depends heavily on correctly factors such as the height of enclosing walls and window
inputting influential parameters such as climatic conditions placement significantly influenced natural air movement
and material properties. and indoor temperature. Such findings underscore the
To increase reliability, CFD simulations must be potential of CFD to predict architectural design solutions
validated through comparison with real-world field that maximize natural ventilation without straining energy
measurements. Combining computational techniques consumption.
with observational data strengthens conclusions and 2.4. Field studies and empirical research on
enhances their relevance for architectural and engineering ventilation performance
applications in sustainable building design. The integration
of CFD results with real-time sensor feedback and In addition to CFD simulations, field measurements and
post-occupancy evaluations represents a promising empirical surveys provide a wealth of information about
development, enabling dynamic calibration and long-term the real-world effectiveness of natural ventilation systems.
performance monitoring. Going forward, cross-validation Field measurements allow researchers to determine how
with empirical field studies and sensitivity analyses across well passive ventilation strategies perform under current
Figure 3. Result of computational fluid dynamics simulation under different weather conditions. Source: Porras-Amores et al., 2019. Copyright © 2019
Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology Elsevier Ltd.
Volume 7 Issue 3 (2025) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.7226