Page 45 - MSAM-1-3
P. 45
Optimization of chemical admixtures for 3DCP
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing
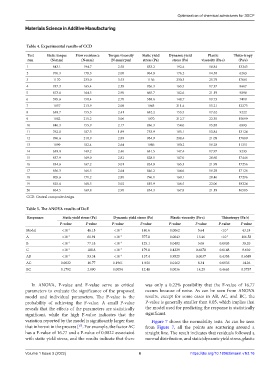
Table 4. Experimental results of CCD
Test Static torque Flow resistance Torque viscosity Static yield Dynamic yield Plastic Thixo‑tropy
run (N∙mm) (N∙mm) (N·mm/rpm) stress (Pa) stress (Pa) viscosity (Pa·s) (Pa/s)
1 843.1 194.7 2.58 833.2 192.4 18.84 13243
2 976.3 178.3 2.00 964.8 176.2 14.58 6263
3 1170 233.0 3.53 1156 230.3 25.79 17081
4 937.3 165.4 2.38 926.3 163.5 17.37 8667
5 673.6 164.5 2.90 665.7 162.6 21.19 9898
6 595.6 150.4 2.70 588.6 148.7 19.73 7410
7 1057 213.9 2.08 1045 211.4 15.21 12373
8 639.7 155.3 2.41 632.2 153.5 17.62 9222
9 1082 215.2 3.06 1070 212.7 22.35 15099
10 846.3 155.9 2.17 836.3 154.0 15.88 6893
11 762.8 187.3 1.89 753.9 185.1 13.84 13124
12 996.6 210.9 2.89 984.9 208.4 21.09 17889
13 1099 182.4 2.64 1086 180.2 19.28 11351
14 639.0 149.2 2.46 631.5 147.4 17.97 9233
15 837.9 169.0 2.82 828.1 167.0 20.60 17446
16 834.6 167.2 3.01 824.8 165.3 21.99 17256
17 856.3 166.5 2.64 846.2 164.6 19.29 17126
18 805.6 171.2 2.80 796.1 169.1 20.46 17296
19 825.6 168.5 3.02 815.9 166.5 22.06 18224
20 864.5 169.8 2.90 854.3 167.8 21.19 16585
CCD: Central composite design
Table 5. The ANOVA results of DoE
Responses Static yield stress (Pa) Dynamic yield stress (Pa) Plastic viscosity (Pa·s) Thixotropy (Pa/s)
P‑value F value P‑value F value P‑value F value P‑value F value
Model <10 -4 46.15 <10 -4 140.6 0.0062 5.64 <10 -4 43.18
A <10 -4 61.91 <10 -4 577.8 0.0043 13.46 <10 -4 106.58
B <10 -4 77.18 <10 -4 125.1 0.0482 5.06 0.0003 30.20
C <10 -4 188.8 <10 -4 179.8 0.4329 0.6678 0.0148 8.630
AB <10 -4 53.34 <10 -4 137.4 0.9525 0.0037 0.4358 0.6589
AC 0.0022 16.77 0.1961 1.920 0.0162 8.34 0.0036 14.26
BC 0.1792 2.090 0.0054 12.48 0.0036 14.29 0.4663 0.5737
In ANOVA, P-value and F-value serve as critical was only a 0.22% possibility that the F-value of 16.77
parameters to evaluate the significance of the proposed occurs because of noise. As can be seen from ANOVA
model and individual parameters. The P-value is the results, except for some cases in AB, AC, and BC, the
probability of achieving the F-value. A small P-value P-value is generally smaller than 0.05, which implies that
reveals that the effects of the parameters are statistically the model used for predicting the response is statistically
significant, while the high F-value indicates that the significant.
variation reported by the model is significantly larger than Figure 7 shows the normability tests. As can be seen
27]
that inherent in the process [ . For example, the factor AC from Figure 7, all the points are scattering around a
has a F-value of 16.77 and a P-value of 0.0022 associated straight line. The result indicates that residuals followed a
with static yield stress, and the results indicate that there normal distribution, and static/dynamic yield stress, plastic
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2022) 6 https://doi.org/10.18063/msam.v1i3.16