Page 76 - TD-3-4
P. 76
Tumor Discovery RNA-protein complexes deregulated in cancer
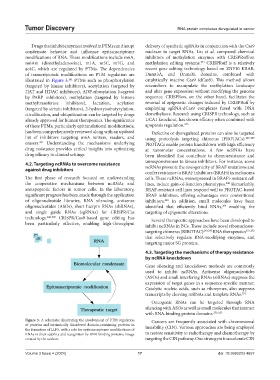
Drugs that inhibit enzymes involved in PTMs can disrupt delivery of synthetic sgRNAs in conjunction with the Cas9
condensate behavior and influence epitranscriptome nuclease to target RNAs. Liu et al. compared chemical
modifications of RNA. These modifications include m6A, inhibitors of methylation enzymes with CRISPRoff/on
m6Am (dimethyladenosine), m1A, m5C, m7G, and methylation editing systems. CRISPRoff is a relatively
244
ac4C, which are regulated by PTMs. The dependencies recent gene editing technology based on ZNF10 KRAB,
of transcriptomic modifications on PTM regulation are Dnmt3A, and Dnmt3L domains, combined with
illustrated in Figure 3. PTMs such as phosphorylation catalytically inactive Cas9 (dCas9). This method allows
241
(targeted by kinase inhibitors), acetylation (targeted by researchers to manipulate the methylation landscape
HAT and HDAC inhibitors), ADP-ribosylation (targeted and alter gene expression without modifying the genome
by PARP inhibitors), methylation (targeted by histone sequence. CRISPRon, on the other hand, facilitates the
methyltransferase inhibitors), lactation, acylation reversal of epigenetic changes induced by CRISPRoff by
(targeted by sirtuin inhibitors), 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation, employing sgRNA-dCas9 complexes fused with DNA
citrullination, and ubiquitination can be targeted by drugs demethylases. Research using CRISPR technology, such as
already approved for human therapeutics. The significance UCA1 knockout, has shown efficacy when combined with
of these PTMs, particularly epitranslational modifications, apoptosis regulation. 245
has been comprehensively reviewed along with an updated Defective or dysregulated proteins can also be targeted
list of inhibitors targeting m6A writers, readers, and using proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs). 245-247
erasers. Understanding the mechanisms underlying PROTACs enable protein knockdown with high efficiency
241
drug resistance provides critical insights into optimizing at nanomolar concentrations. A few ncRNAs have
drug efficacy in clinical settings. been identified that contribute to chemoresistance and
unresponsiveness to kinase inhibitors. For instance, some
4.2. Targeting ncRNAs to overcome resistance ncRNAs promote the oncogenicity of BRAF mutations and
against drug inhibitors
confer resistance to BRAF inhibitors (BRAFi) in melanoma
The first phase of research focused on understanding cells. These ncRNAs, overexpressed in BRAFi-resistant cell
the cooperative mechanisms between ncRNAs and lines, induce gain-of-function phenotypes. Remarkably,
248
antiapoptotic factors in tumor cells. In the laboratory, BRAF-resistant cell lines respond well to PROTAC-based
significant progress has been made through the application BRAF inhibition, offering advantages over conventional
of oligonucleotide libraries, RNA silencing, antisense inhibitors. In addition, small molecules have been
249
oligonucleotides (ASOs), short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs), identified that efficiently bind RNAs, enabling the
206
and single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) for CRISPR/Cas targeting of epigenetic alterations.
technology. 242-245 CRISPR/Cas9-based gene editing has Several therapeutic approaches have been developed to
been particularly effective, enabling high-throughput
inhibit ncRNAs in BCs. These include novel ribonuclease-
targeting chimeras (RIBOTAC) 249,250 RNA therapeutics 251,252
that selectively regulate RNA-modifying enzymes, and
targeting major SG proteins.
4.3. Targeting the mechanisms of therapy resistance
by ncRNA knockdown
Gene silencing and knockdown methods are commonly
used to inhibit ncRNAs. Antisense oligonucleotides
(ASOs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) suppress the
expression of target genes in a sequence-specific manner.
Catalytic nucleic acids, such as ribozymes, also suppress
transcripts by cleaving mRNAs and template RNAs. 251
Oncogenic RNAs can be targeted through RNA
silencing with ASOs as well as small molecules that interact
with RNA-binding protein domains. 252-255
Figure 3. A schematic illustrating the involvement of PTM regulation Cancers are frequently associated with chromosomal
of proteins and intrinsically disordered domain-containing proteins in instability (CIN). Various approaches are being employed
the formation of LLPS, with a role for epitranscriptome modifications of
RNAs in their stability and recognition by RNA-binding proteins. Image to restore sensitivity to radiotherapy and chemotherapy by
created by the authors targeting the CIN pathway. One strategy is to accelerate CIN
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 17 doi: 10.36922/td.4657