Page 118 - AIH-1-2
P. 118
Artificial Intelligence in Health Medical instruction-tuning for Japanese LLMs
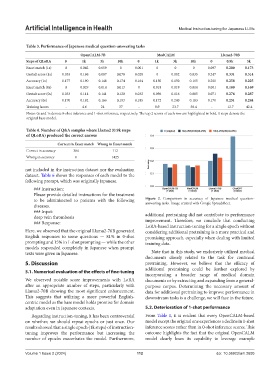
Table 3. Performance of Japanese medical question‑answering tasks
OpenCALM‑7B MedCALM Llama2‑70B
Steps of QLoRA 0 1k 3k 10k 0 1k 3k 10k 0 0.9k 3k
Exact match (1s) 0 0.042 0.059 0 0.001 0 0 0 0.097 0.200 0.173
Gestalt score (1s) 0.053 0.186 0.087 0.078 0.028 0 0.002 0.035 0.247 0.331 0.314
Accuracy (1s) 0.177 0.190 0.148 0.174 0.164 0.150 0.150 0.165 0.200 0.258 0.225
Exact match (0s) 0 0.029 0.014 0.013 0 0.018 0.019 0.014 0.001 0.180 0.169
Gestalt score (0s) 0.033 0.114 0.141 0.120 0.032 0.096 0.116 0.085 0.071 0.276 0.287
Accuracy (0s) 0.170 0.182 0.166 0.193 0.185 0.172 0.240 0.183 0.170 0.251 0.244
Training hours - 4.6 24 37 - 8.9 23.7 58.4 - 12.7 42.4
Notes: 0s and 1s denote 0-shot inference and 1-shot inference, respectively. The top 2 scores of each row are highlighted in bold. 0 steps denote the
original base model.
Table 4. Number of Q&A samples where Llama2 (0.9k steps
of QLoRA) produced the correct answer
Correct in Exact match Wrong in Exact match
Correct in accuracy 384 112
Wrong in accuracy 0 1425
not included in the instruction dataset nor the evaluation
dataset. Table 6 shows the responses of each model to the
following prompt, which was originally Japanese.
### Instruction:
Please provide detailed instructions for the treatment
to be administered to patients with the following Figure 2. Comparison in accuracy of Japanese medical question-
answering tasks. Image created with Google Spreadsheet.
diseases.
### Input: additional pretraining did not contribute to performance
deep vein thrombosis
### Response: improvement. Therefore, we conclude that conducting
LoRA-based instruction-tuning for a single epoch without
Here, we observed that the original Llama2-70B generated considering additional pretraining is a more practical and
English responses to some questions — 81% in 0-shot promising approach, especially when dealing with limited
prompting and 15% in 1-shot prompting — while the other training data.
models responded completely in Japanese when prompt
texts were given in Japanese. Note that in this study, we exclusively utilized medical
documents closely related to the task for continual
5. Discussion pretraining. However, we believe that the efficacy of
additional pretraining could be further explored by
5.1. Numerical evaluation of the effects of fine-tuning
incorporating a broader range of medical domain
We observed notable score improvements with LoRA documents or by extracting and expanding from a general-
after an appropriate number of steps, particularly with purpose corpus. Determining the necessary amount of
Llama2-70B showing the most significant enhancement. data for additional pretraining to improve performance in
This suggests that utilizing a more powerful English- downstream tasks is a challenge, we will face in the future.
centric model as the base model holds promise for domain
adaptation even in Japanese contexts. 5.2. Deterioration of 1-shot performance
Regarding instruction-tuning, it has been controversial From Table 1, it is evident that every OpenCALM-based
on whether, we should repeat epochs or just once. Our model except the original one experiences a decline in 1-shot
results showed that a single epoch (1k steps) of instruction- inference scores rather than in 0-shot inference scores. This
tuning improves the performance but increasing the outcome highlights the fact that the original OpenCALM
number of epochs exacerbates the model. Furthermore, model clearly loses its capability to leverage example
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 112 doi: 10.36922/aih.2695