Page 98 - AIH-1-4
P. 98
Artificial Intelligence in Health Transformer-based radiology report summaries
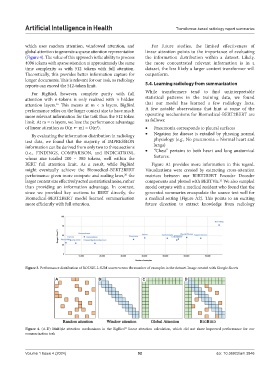
which uses random attention, windowed attention, and For future studies, the limited effectiveness of
global attention to generate a sparse attention representation linear attention points to the importance of evaluating
(Figure 4). The value of this approach is the ability to process the information distribution within a dataset. Likely,
4096 tokens with sparse attention at approximately the same the more concentrated relevant information is in a
time complexity as with 512 tokens with full attention. dataset, the less likely a larger context transformer will
Theoretically, this provides better information capture for outperform.
longer documents. This is relevant for our task, as radiology
reports can exceed the 512-token limit. 5.4. Learning radiology from summarization
For BigBird, however, complete parity with full While transformers tend to find uninterpretable
attention with n-tokens is only realized with n hidden statistical patterns in the training data, we found
16
attention layers. This means at m < n layers, BigBird that our model has learned a few radiology facts.
performance relies on the larger context size to have much A few notable observations that hint at some of the
more relevant information for the task than the 512 token operating mechanisms for Biomedical-BERT2BERT are
limit. At m = n layers, we lose the performance advantage as follows:
of linear attention as O(n ⇤ m) = O(n ). • Pneumonia corresponds to pleural surfaces
2
By evaluating the information distribution in radiology • Negation for disease is entailed by phrasing normal
text data, we found that the majority of IMPRESSION physiology (e.g., No pneumonia = Normal heart and
information can be derived from only two to three sections lungs)
(i.e., FINDINGS, COMPARISON, and INDICATION), • “Chest” pertains to both heart and lung anatomical
whose size totaled 200 – 300 tokens, well within the features.
BERT full attention limit. As a result, while BigBird Figure A1 provides more information in this regard.
might eventually achieve the Biomedical-BERT2BERT Visualizations were created by extracting cross-attention
performance given more compute and scaling laws, the matrices between our BERT2BERT Encoder Decoder
20
larger context size effectively acted as statistical noise, rather components and plotted with BERTViz. We also sampled
21
than providing an information advantage. In contrast, model outputs with a medical resident who found that the
since we provided key sections to BERT directly, the generated summaries encapsulate the source text well for
Biomedical-BERT2BERT model learned summarization a medical setting (Figure A2). This points to an exciting
more efficiently with full attention. future direction to extract knowledge from radiology
Figure 3. Performance distribution of ROUGE-L SUM scores versus the number of examples in the dataset. Image created with Google Sheets
A B C D
Figure 4. (A-D) Multiple attention mechanisms in the BigBird linear attention calculation, which did not show improved performance for our
16
summarization task
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2024) 92 doi: 10.36922/aih.3846