Page 53 - {PDF Title}
P. 53
Bioremediation of river water using Moringa oleifera seed extract
A B
C D
E F
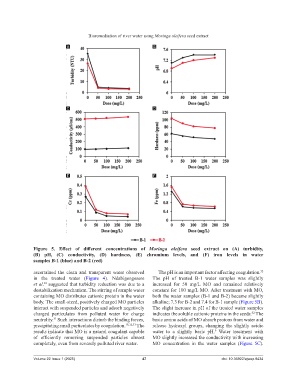
Figure 5. Effect of different concentrations of Moringa oleifera seed extract on (A) turbidity,
(B) pH, (C) conductivity, (D) hardness, (E) chromium levels, and (F) iron levels in water
samples B‑1 (blue) and B‑2 (red)
ascertained the clean and transparent water observed The pH is an important factor affecting coagulation.
32
in the treated water (Figure 4). Ndabigengesere The pH of treated B-1 water samples was slightly
et al. suggested that turbidity reduction was due to a increased for 50 mg/L MO and remained relatively
30
destabilization mechanism. The stirring of sample water constant for 100 mg/L MO. After treatment with MO,
containing MO distributes cationic protein in the water both the water samples (B-1 and B-2) became slightly
body. The small-sized, positively charged MO particles alkaline; 7.3 for B-2 and 7.4 for B-1 sample (Figure 5B).
interact with suspended particles and adsorb negatively The slight increase in pH of the treated water samples
charged particulates from polluted water for charge indicates the soluble cationic proteins in the seeds. The
32
neutrality. Such interactions disturb the binding forces, basic amino acids of MO absorb protons from water and
31
precipitating small particulates by coagulation. 18,32,33 The release hydroxyl groups, changing the slightly acidic
results indicate that MO is a natural coagulant capable water to a slightly basic pH. Water treatment with
9
of efficiently removing suspended particles almost MO slightly increased the conductivity with increasing
completely, even from severely polluted river water. MO concentration in the water samples (Figure 5C).
Volume 22 Issue 1 (2025) 47 doi: 10.36922/ajwep.8434