Page 33 - AN-1-1
P. 33
Advanced Neurology Gastrointestinal symptoms in PD
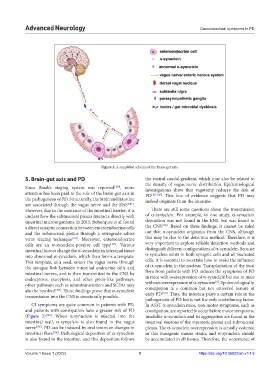
Figure 2. A simplified schema of the brain-gut axis.
5. Brain-gut axis and PD the rostral-caudal gradient, which may also be related to
the density of vagus nerve distribution. Epidemiological
Since Braak’s staging system was reported [100] , more investigations show that vagotomy reduces the risk of
attention has been paid to the role of the brain-gut axis in PD [107,108] . This line of evidence suggests that PD may
the pathogenesis of PD. Structurally, the brain and intestine indeed originate from the intestine.
are associated through the vagus nerve and the ENS [101] .
However, due to the existence of the intestinal barrier, it is There are still some questions about the transmission
unclear how the submucosal plexus interacts directly with of α-synuclein. For example, in one study, α-synuclein
intestinal microorganisms. In 2015, Bohorquez et al. found deposition was not found in the ENS, but was found in
a direct synaptic connection between enteroendocrine cells the CNS [109] . Based on these findings, it cannot be ruled
and the submucosal plexus through a retrograde rabies out that α-synuclein originates from the CNS, although
virus tracing technique [102] . Moreover, enteroendocrine this may be due to the detection method. Therefore, it is
cells are an α-synuclein-positive cell type [103] . Various very important to explore reliable detection methods and
intestinal factors change the α-synuclein in intestinal tissue distinguish different configurations of α-synuclein. Because
into abnormal α-synuclein, which then forms a template. α-synuclein exists in both synaptic cells and all nucleated
This template, as a seed, enters the vagus nerve through cells, it is essential to ascertain how to avoid the influence
the synapse link between intestinal endocrine cells and of α-synuclein in the nucleus. Transplantation of the fecal
intestinal nerves, and is then transmitted to the CNS by flora from patients with PD induces the symptoms of PD
endocytosis, exocytosis, and other prion-like pathways; in mice with overexpression of α-synuclein but not in mice
[6]
other pathways such as neurotransmitters and SCFAs may without overexpression of α-synuclein . Epidemiologically,
also be involved [101] . These findings prove that α-synuclein constipation is a common but not universal feature of
[110]
transmission into the CNS is structurally possible. early PD . Thus, the intestine plays a certain role in the
pathogenesis of PD but is not the only contributing factor.
GI symptoms are quite common in patients with PD, In A53T α-synuclein mice, non-motor symptoms, such as
and patients with constipation have a greater risk of PD constipation, are reported to occur before motor symptoms.
(Figure 2) [104] . When α-synuclein is injected into the Insoluble α-synuclein and its aggregation are found in the
intestinal wall, α-synuclein is also found in the vagus intestinal neurons of the myenteric plexus and submucosal
nerve [105] . PD can be induced by oral toxins or changes in plexus. The α-synuclein overexpression is actually systemic
intestinal flora [106] . Pathological deposition of α-synuclein in this transgenic mouse strain, and α-synuclein should
is also found in the intestine, and this deposition follows be accumulated in all tissues. Therefore, the occurrence of
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2022) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v1i1.9