Page 86 - AN-1-1
P. 86
Advanced Neurology TRPM2 in neurological disorders
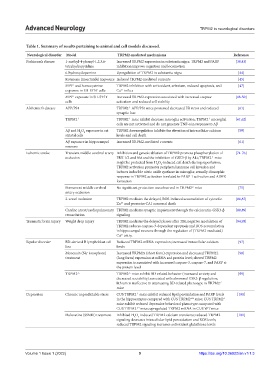
Table 1. Summary of results pertaining to animal and cell models discussed.
Neurological disorder Model TRPM2-mediated mechanisms Reference
Parkinson’s disease 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6- Increased TRPM2 expression in substantia nigra; TRPM2 and PARP [38,43]
tetrahydropyridine inhibition improve cognition and locomotion
6-hydroxydopamine Upregulation of TRPM2 in substantia nigra [44]
Rotenone (insecticide) Exposure Induced TRPM2-mediated currents [45]
MPP and homocysteine TRPM2 inhibition with antioxidant, selenium, reduced apoptosis, and [47]
+
exposure in SH-SY5Y cells Ca -influx
2+
MPP exposure in SH-SY5Y Increased TRPM2 expression associated with increased caspase [48-50]
+
cells activation and reduced cell viability
Alzheimer’s disease APP/PS1 TRPM2 APP/PS1 mice possessed decreased ER stress and reduced [61]
-/-
synaptic loss
TRPM2 -/- TRPM2 mice exhibit decrease microglia activation; TRPM2 microglial [61,62]
-/-
-/-
cells are not activated and do not generate TNF-α in response to Aβ
Aβ and H O exposure in rat TRPM2 downregulation inhibits the elevation of intracellular calcium [59]
2
2
striatal cells levels and cell death
Aβ exposure in hippocampal Increased TRPM2-mediated currents [61]
neurons
Ischemic stroke Transient middle cerebral artery Inhibition and genetic ablation of TRPM2 promote phosphorylation of [74-76]
occlusion ERK 1/2 and Akt and the inhibition of GSK3-β by Akt; TRPM2 mice
-/-
might be protected from H O -induced cell death during reperfusion;
2
2
TRPM2 activation promotes peripheral immune cell invasion and
induces inducible nitric oxide synthase in microglia; sexually dimorphic
response in TRPM2 activation is related to PARP-1 activation and ADPR
formation
Permanent middle cerebral No significant protection was observed in TRPM2 mice [75]
-/-
artery occlusion
2-vessel occlusion TRPM2 mediates the delayed, ROS-induced accumulation of cytosolic [86,87]
Zn and promotes CA1 neuronal death
2+
Cardiac arrest/cardiopulmonary TRPM2 mediates synaptic impairment through the calcineurin-GSK3-β [88,89]
resuscitation signaling
Traumatic brain injury Weight drop injury TRPM2 mediates the delayed phases after TBI; negative modulation of [94,95]
TRPM2 reduces caspase-3-dependent apoptosis and ROS accumulation
in hippocampal neurons through the regulation of (TRPM2-mediated)
Ca entry.
2+
Bipolar disorder BD-derived B lymphoblast cell Reduced TRPM2 mRNA expression; increased intracellular calcium [97]
line levels
+
Monensin (Na ionophore) Increased TRPM2s (short form) expression and decreased TRPM2L [98]
treatment (long form) expression at mRNA and protein level; altered TRPM2
expression is associated with increased caspase-3, caspase-7, and PARP at
the protein level
TRPM2 -/- TRPM2 mice exhibit BD-related behavior (increased anxiety and [99]
-/-
decreased sociability) associated with abnormal GSK3-β regulation;
lithium is ineffective in attenuating BD-related phenotype in TRPM2
-/-
mice
Depression Chronic unpredictable stress CUS TRPM2 mice exhibit reduced lipid peroxidation and PARP levels [100]
-/-
in the hippocampus compared with CUS TRPM2 mice; CUS TRPM2 -/-
+/+
mice exhibit reduced depressive behavioral phenotype compared with
CUS TRPM2 mice; upregulated TRPM2 mRNA in CUS WT mice
+/+
Duloxetine (SSNRI) treatment Inhibited H O -induced TRPM2 calcium transients; reduced TRPM2 [101]
2
2
signaling decreases intracellular lipid peroxidation and ROS levels;
reduced TRPM2 signaling increases antioxidant glutathione levels
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2022) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v1i1.3