Page 31 - AN-1-3
P. 31
Advanced Neurology Inflammation and gut microbiota in depression
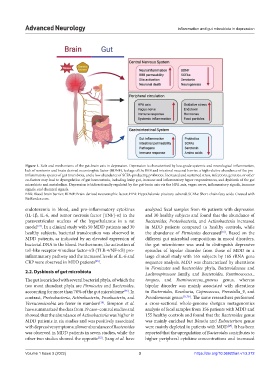
Figure 1. Role and mechanisms of the gut-brain axis in depression. Depression is characterized by low-grade systemic and neurological inflammation,
lack of serotonin and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), leakage of the BBB and intestinal mucosal barrier, a high relative abundance of the pro-
inflammatory species of gut microbiota, and a low abundance of SCFA-producing probiotics. Increased and sustained stress, infections, genetics, or other
co-factors may lead to dysregulation of gut homeostasis, including leaky gut, immune and inflammatory hyper responsiveness, and dysbiosis of the gut
microbiota and metabolism. Depression is bidirectionally regulated by the gut-brain axis via the HPA axis, vagus nerve, inflammatory signals, immune
signals, and chemical signals.
BBB: Blood-brain barrier; BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; HPA: Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal; SCFAs: Short-chain fatty acids. Created with
BioRender.com.
endotoxemia in blood, and pro-inflammatory cytokines analyzed fecal samples from 46 patients with depression
(IL-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor [TNF]-α) in the and 30 healthy subjects and found that the abundance of
paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in a rat Bacteroides, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria increased
[24]
model . In a clinical study with 50 MDD patients and 30 in MDD patients compared to healthy controls, while
healthy subjects, bacterial translocation was observed in the abundance of Firmicutes decreased . Based on the
[16]
MDD patients, as indicated by an elevated expression of different gut microbial compositions in mood disorders,
bacterial DNA in the blood. Furthermore, the activation of the gut microbiome was used to distinguish depressive
toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-κB (TLR-4/NF-κB) pro- episodes of bipolar disorder from those of MDD in a
inflammatory pathway and the increased levels of IL-6 and large clinical study with 165 subjects by 16S rRNA gene
CRP were observed in MDD patients . sequence analysis. MDD was characterized by alterations
[25]
in Firmicutes and Bacteroides phyla, Bacteroidaceae and
2.2. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota Lachnospiraceae family, and Bacteroides, Ruminococcus_
The gut is enriched with several bacterial phyla, of which the torques, and Ruminococcus_gnavus genus, whereas
two most abundant phyla are Firmicutes and Bacteroides, bipolar disorder was mainly associated with alterations
accounting for more than 70% of the gut microbiome . In in Bacteroides, Roseburia, Coprococcus, Prevotella_9, and
[26]
contrast, Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Fusobacteria, and Pseudomonas genus [27,28] . The same researchers performed
Verrucomicrobia are fewer in numbers . Simpson et al. a cross-sectional whole-genome shotgun metagenomics
[26]
have summarized the data from 19 case–control studies and analysis of fecal samples from 156 patients with MDD and
showed that the abundance of Actinobacteria was higher in 155 healthy controls and found that the Bacteroides genus
MDD patients in six studies and was positively associated was mainly enriched but Blautia and Eubacterium genus
with depressive symptoms; a lower abundance of Bacteroides were mainly depleted in patients with MDD . It has been
[29]
was observed in MDD patients in seven studies, while the reported that the upregulation of Bacteroides contributes to
other two studies showed the opposite . Jiang et al. have higher peripheral cytokine concentrations and increased
[12]
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2022) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v1i3.272