Page 49 - AN-1-3
P. 49
Advanced Neurology The diagnosis and treatment of anti-LGI1 autoimmune encephalitis
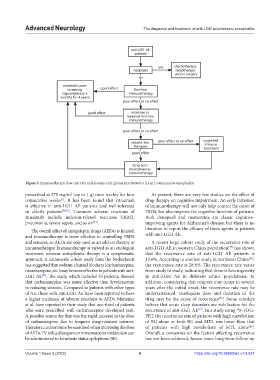
Figure 2. Immunotherapy flow chart for anti-leucine-rich glioma inactivated-1 (LGI1) autoimmune encephalitis.
prescribed at 375 mg/m (up to 1 g) once weekly for four At present, there are very few studies on the effect of
2
consecutive weeks . It has been found that rituximab drug therapy on cognitive impairment. An early initiation
[1]
is effective in anti-LGI1 AE patients and well-tolerated of immunotherapy will not only help control the onset of
in elderly patients [74,75] . Common adverse reactions of FBDS, but also improve the cognitive function of patients.
rituximab include infusion-related reactions (IRRS), Both donepezil and memantine are classic cognitive-
pneumonia, severe sepsis, and so on . improving agents for Alzheimer’s disease, but there is no
[44]
The overall effect of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) is limited, literature to report the efficacy of these agents in patients
and immunotherapy is more effective in controlling FBDS with anti-LGI1 AE.
and seizures, so AEDs are only used as an add-on therapy to A recent large cohort study of the recurrence rate of
immunotherapy. Immunotherapy is viewed as an etiological anti-LGI1 AE in western China population has shown
[77]
treatment, whereas antiepileptic therapy is a symptomatic that the recurrence rate of anti-LGI1 AE patients is
approach. A nationwide cohort study from the Netherlands 13.6%. According to another study in northeast China ,
[64]
has suggested that sodium channel blockers (carbamazepine, the recurrence rate is 28.6%. The recurrence rate varies
oxcarbazepine, etc.) may be more effective in patients with anti- from study to study, indicating that there is heterogeneity
LGI1 AE . The study, which included 53 patients, showed in anti-LGI1 AE in different ethnic populations. In
[76]
that carbamazepine was more effective than levetiracetam addition, considering that relapses may occur in several
in reducing seizures. Compared to patients with other types years after the initial onset, the recurrence rate may be
of AE, those with anti-LGI1 AE have been reported to have underestimated. Inadequate dose and duration of the
[32]
a higher incidence of adverse reactions to AEDs. Marienke drug may be the cause of recurrence . Some scholars
et al. have reported in their study that one-third of patients believe that acute sleep disorders are risk factors for the
[77]
who were prescribed with carbamazepine developed rash. recurrence of anti-LGI1 AE . In a study using F-FDG-
18
A possible reason for that was the rapid increase in the dose PET, the recurrence rate of patients with high metabolism
of carbamazepine due to frequent drug-resistant seizures. of BG alone or both BG and MTL was lower than that
Therefore, caution must be exercised when increasing the dose of patients with high metabolism of MTL alone .
[42]
of AEDs. IV bolus diazepam or intramuscular midazolam can Overall, a consensus on the factors affecting recurrence
be administered to terminate status epilepticus (SE). has not been achieved; hence, more long-term follow-up
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2022) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v1i3.237