Page 49 - AN-2-1
P. 49
Advanced Neurology Piribedil for Parkinson’s disease
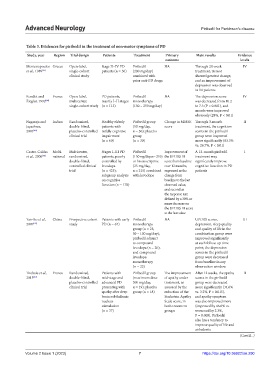
Table 3. Evidences for piribedil in the treatment of non‑motor symptoms of PD
Study, year Region Trial design Patients Treatment Primary Main results Evidence
outcome levela
Mentenopoulos Greece Open-label, Stage II–IV PD Piribedil NA Through 20-week IV
et al., 1989 [45] single-cohort patients (n = 30) (200 mg/day) treatment, tremor
clinical study combined with showed greatest change,
prior anti-PD drugs and an improvement of
depression was observed
in 14 patients
Rondot and France Open-label, PD patients, Piribedil NA The depression score IV
Ziegler, 1992 [40] multicenter, mainly I–II stages monotherapy was decreased from 10.2
single-cohort study (n = 113) (150 – 250 mg/day) to 7.3 (P < 0.001), and
moods were improved
obviously (28%, P < 0.01)
Nagaraja and Indian Randomized, Healthy elderly Piribedil group Change in MMSE Through 3-month II
Jayashree, double-blind, patients with (50 mg/day, score treatment, the cognition
2001 [46] placebo-controlled mildly cognitive n = 30); placebo scores in the piribedil
clinical trial impairment group group were improved
(n = 60) (n = 30) more significantly (63.3%
vs. 26.7%, P < 0.01)
Castro-Caldas Multi- Multicenter, Stages I–III PD Piribedil Improvement of A 12-month piribedil I
et al., 2006 [38] national randomized, patients, poorly (150 mg/day, n = 210) the UPDRS III treatment may
double-blind, controlled by or bromocriptine score from baseline significantly improve
controlled clinical levodopa (25 mg/day, over 12 months, cognitive function in PD
trial (n = 425); n = 215) combined expressed as the patients
subgroup analysis with levodopa change from
on cognitive baseline to the last
function (n = 178) observed value,
and second as
the response rate
defined by a 30% or
more decrease on
the UPDRS III score
at the last value
Yan-Bo et al., China Prospective cohort Patients with early Piribedil NA UPDRS scores, III
2007 [72] study PD (n = 67) monotherapy depression, sleep quality
group (n = 25, and quality of life in the
50 – 100 mg/day); combination group were
piribedil adjunct improved significantly
to compound at each follow-up time
levodopa (n = 20); point; the depression
and compound scores in the piribedil
levodopa group were decreased
monotherapy from baseline in any
(n = 22) observation window
Thobois et al., France Randomized, Patients with Piribedil group The improvement After 12 weeks, the apathy II
2013 [47] double-blind, mid-stage and (maximum dose of apathy under scores in the piribedil
placebo-controlled advanced PD 300 mg/day, treatment, as group were decreased
clinical trial presenting with n = 19); placebo assessed by the more significantly (34.6%
apathy after deep group (n = 18) reduction of the vs. 3.2%, P = 0.015),
brain subthalamic Starkstein Apathy and apathy symptom
nucleus Scale score, in was also improved more
stimulation both treatment (improved by 46.6% vs.
(n = 37) groups worsened by 2.3%,
P = 0.005). Piribedil
also has a tendency to
improve quality of life and
anhedonia
(Cont’d...)
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.290