Page 71 - AN-2-1
P. 71
Advanced Neurology Alpha-synuclein, depression and neurodegeneration
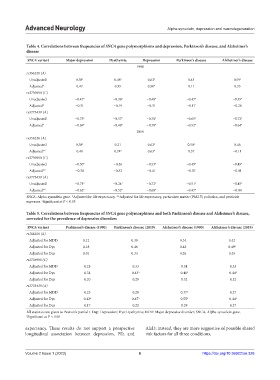
Table 4. Correlations between frequencies of SNCA gene polymorphisms and depression, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s
disease
SNCA variant Major depression Dysthymia Depression Parkinson’s disease Alzheimer’s disease
1990
rs356220 (A)
Unadjusted 0.58 a 0.48 a 0.62 a 0.43 0.59 a
Adjusted* 0.47 0.35 0.50 a 0.11 0.35
rs2736990 (C)
Unadjusted −0.47 a −0.36 a −0.48 a −0.47 a −0.55 a
Adjusted* −0.31 −0.19 −0.31 −0.17 −0.28
rs3775439 (A)
Unadjusted −0.75 a −0.57 a −0.76 a −0.65 a −0.72 a
Adjusted* −0.69 a −0.48 a −0.70 a −0.52 a −0.64 a
2019
rs356220 (A)
Unadjusted 0.58 a 0.21 0.62 a 0.50 a 0.46
Adjusted** 0.48 0.74 a 0.63 a 0.37 −0.11
rs2736990 (C)
Unadjusted −0.50 a −0.26 −0.53 a −0.49 a −0.45 a
Adjusted** −0.38 −0.32 −0.41 −0.07 −0.01
rs3775439 (A)
Unadjusted −0.71 a −0.24 a −0.72 a −0.51 a −0.45 a
Adjusted** −0.62 a −0.52 a −0.68 a −0.47 a −0.04
SNCA: Alpha-synuclein gene. *Adjusted for life expectancy. **Adjusted for life expectancy, particulate matter (PM2.5) pollution, and pesticide
exposure. Significant at P < 0.05
a
Table 5. Correlations between frequencies of SNCA gene polymorphisms and both Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease,
corrected for the prevalence of depressive disorders
SNCA variant Parkinson’s disease (1990) Parkinson’s disease (2019) Alzheimer’s disease (1990) Alzheimer’s disease (2019)
rs356220 (A)
Adjusted for MDD 0.12 0.39 0.34 0.42
Adjusted for Dys 0.18 0.46 0.42 0.49 a
Adjusted for Dep 0.01 0.34 0.26 0.45
rs2736990 (C)
Adjusted for MDD −0.23 −0.33 −0.34 −0.33
Adjusted for Dys −0.34 −0.43 a −0.46 a −0.44 a
Adjusted for Dep −0.20 −0.29 −0.32 −0.32
rs3775439 (A)
Adjusted for MDD −0.25 −0.28 −0.37 a −0.27
Adjusted for Dys −0.42 a −0.47 a −0.55 a −0.44 a
Adjusted for Dep −0.17 −0.22 −0.29 −0.27
All statistics are given as Pearson’s partial r. Dep: Depression; Dys: Dysthymia; MDD: Major depressive disorder; SNCA, Alpha-synuclein gene.
a Significant at P < 0.05
expectancy. These results do not support a prospective AlzD; instead, they are more suggestive of possible shared
longitudinal association between depression, PD, and risk factors for all three conditions.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.326