Page 59 - AN-3-1
P. 59
Advanced Neurology Dementia with Lewy bodies and substance misuse
A B The LC is also sometimes involved. Pick bodies and tau
aggregates can be found, often in the hippocampus, the
Sommer’s sector, subiculum, and olfactory bulb, as well
as the entorhinal, frontal, temporal, cingulate, and insular
cortices. 89
CSF analysis of biological markers can help detect the
presence of aggresomes in AD, FTD, vascular dementia
(VD), and DLB. When β-amyloid clumps to form plaques,
there is less free β-amyloid available to diffuse into the
CSF, resulting in lower levels of Aβ42 in the CSF. T-tau
40
and p-tau are increased in AD but can be normal or only
mildly increased in FTD, VD, and DLB. Aβ42 is usually
normal-to-moderately decreased in FTD and VD but
moderately decreased in Lewy body dementia. 40,41 By
contrast, uncomplicated alcohol-related dementia and
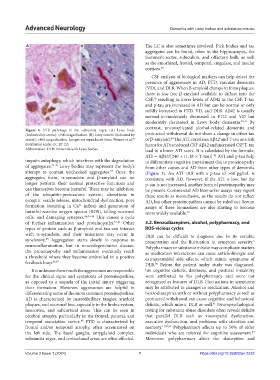
Figure 4. DLB pathology in the substantia nigra. (A) Lewy body
(indicated by arrow), ×500 magnification. (B) Lewy neurite (indicated by protracted withdrawal do not show a change in either tau
40
arrow), ×400 magnification. Images are reproduced from Werner et al. or β-amyloid. The ATI correlates Aβ42 and T-tau as a risk
54
distributed under CC BY 2.0. factor for AD; a reduced CSF Aβ42 and increased CSF T-tau
Abbreviation: DLB: Dementia with Lewy bodies. lead to a lower ATI score. It is calculated by the formula:
ATI = Aβ42/[240 + (1.18 × T-tau)]. ATI and p-tau help
42
impairs autophagy, which interferes with the degradation to differentiate cognitive impairment due to proteinopathy
of aggregates. 73-76 Lewy bodies may represent the body’s from other causes and AD from other types of dementia
67
attempt to contain unchecked aggregates. Once the (Figure 1). An ATI <0.8 with a p-tau of >68 pg/mL is
aggregates form, α-synuclein and β-amyloid can no consistent with AD. However, if the ATI is low, but the
longer perform their normal protective functions and p-tau is not increased, another form of proteinopathy may
can themselves become harmful. There may be inhibition be present. Commercial AD biomarker assays may report
of the ubiquitin-proteasome system, alterations in these results as inconclusive, as the results do not reflect
synaptic vesicle release, mitochondrial dysfunction, pore AD, but other proteinopathies cannot be ruled out. Serum
formation (resulting in Ca influx) and generation of assays of these biomarkers are also starting to become
2+
harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS), killing neuronal more widely available. 43
cells, and damaging synapses. 64,76-80 This causes a cycle
of further inflammation and proteinopathy. 81-84 Other 3.2. Benzodiazepines, alcohol, polypharmacy, and
types of protein such as β-amyloid and tau can interact ROS-vicious cycles
with α-synuclein, and their mutations may occur in DLB can be difficult to diagnose due to its variable
synchrony. Aggregation starts slowly in response to presentation and the fluctuation in symptom severity.
85
3
neuroinflammation, but in neurodegenerative disease, Polypharmacy or substance misuse may complicate matters
the proteinopathy and inflammation eventually reach as medication interactions can cause anticholinergic and
a threshold where they become embroiled in a positive extrapyramidal side effects, which mimic symptoms of
feedback loop. 86,87 DLB. Before the patient under study was diagnosed,
90
It is unknown how much the aggresomes are responsible his cognitive deficits, dizziness, and postural instability
for the clinical signs and symptoms of proteinopathies, were attributed to his polypharmacy and were not
as opposed to a sequela of the initial injury triggering recognized as features of DLB. Fluctuations in symptoms
their formation. However, aggresomes are helpful in may be attributed to changes in medication. Alcohol and
differentiating some of the more common proteinopathies. benzodiazepines with or without polypharmacy as well as
AD is characterized by neurofibrillary tangles, amyloid protracted withdrawal can cause cognitive and behavioral
plaques, and neuronal loss, especially in the limbic system, deficits, which mimic DLB as well. Neuropsychological
91
neocortex, and subcortical areas. This can be seen in testing for substance abuse disorders often reveals deficits
cerebral atrophy, particularly in the frontal, parietal, and that parallel DLB such as visuospatial dysfunction,
temporal association cortex. FTD is characterized by executive dysfunction, and problems with attention and
88
frontal and/or temporal atrophy, often accentuated on memory. 11,92,93 Polypharmacy affects up to 50% of older
the left side. The basal ganglia, amygdaloid complex, individuals who are referred for cognitive assessment.
94
substantia nigra, and corticobasal areas are often affected. Moreover, polypharmacy alters the absorption and
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.2232