Page 86 - AN-3-1
P. 86
Advanced Neurology Neurophysiology in hypokinetic disorders
Table 2. Summary of the neurophysiological insights of studies reported from 2019 to 2023 on atypical Parkinsonian syndromes
Atypical Parkinsonian Neurophysiological assessment Neurophysiological insights Studies
syndrome
MSA EMG
Diurnal kinesiologic study of (i). MSA-P displayed a dystonic pattern associated with Todisco et al. 30
the adductor thyroarytenoid nocturnal stridor
and the abductor posterior (ii). MSA-C displayed a dystonic-plus pattern, presented with
cricoarytenoid muscles additional neurogenic findings
External anal sphincter study Electrophysiological impairment severity paralleled diagnostic Todisco et al. 31
accuracy and MSA prognosis
TMS Decreased CBI in MSA-C with a significant correlation with the Shirota et al. 32
degree of ataxia
R2BRRC Symmetrical pattern of brainstem excitability observed and Sciacca et al. 38
decreased AI
PSP TMS (i) Degree of LTP impairment reflects the severity of (i) Honda et al. 33
bradykinesia in Richardson phenotype (ii) Fisicaro et al. 34
(ii) Increased MEP amplitude, increased CSP latency, and
normal CMCT in drug-naïve patients.
R2BRRC Symmetrical pattern of brainstem excitability and decreased AI. Sciacca et al. 38
CBS R2BRRC (i) A cut-off value greater than 33% differentiated CBS from Sciacca et al. 37
PSP; a cut-off value of 23% distinguished CBS from MSA Donzuso et al. 39
(ii) AI of R2BRRC is associated with the AI of MRI: PD exhibited
an asymmetrical pattern of brainstem excitability, whereas
CBS displayed an asymmetrical pattern of cortical atrophy
Abbreviations: AI: Asymmetry index; CBI: Cerebellar inhibition; CBS: Corticobasal syndrome; CMCT: Central motor conduction time; CSP: Cortical
silent period; EMG: Electromyography; LTP: Long-term potentiation; MEP: Motor evoked potential; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; MSA: Multiple
system atrophy; MSA-C: Multiple system atrophy with a cerebellar phenotype; MSA-P: Multiple system atrophy with Parkinsonian phenotype;
PD: Parkinson’s disease; PSP: Progressive supranuclear palsy; TMS: Transcranial magnetic stimulation; R2BRRC: R2 blink reflex recovery cycle.
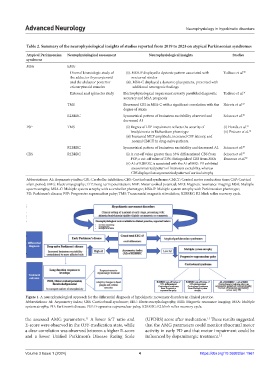
Figure 1. A neurophysiological approach for the differential diagnosis of hypokinetic movement disorders in clinical practice.
Abbreviations: AI: Asymmetry index; CBS: Corticobasal syndrome; EEG: Electroencephalography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; MSA: Multiple
system atrophy; PD: Parkinson’s disease; PSP: Progressive supranuclear palsy; R2BRRC: R2 blink reflex recovery cycle.
the assessed AMG parameters. A lower S/T ratio and (UPDRS) score after medication. These results suggested
11
11
E-score were observed in the OFF-medication state, while that the AMG parameters could monitor abnormal motor
a clear correlation was observed between a higher E-score activity in early PD and that motor impairment could be
and a lower Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale influenced by dopaminergic treatment. 11
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.1961