Page 27 - AN-4-2
P. 27
Advanced Neurology SARS-CoV-2 mechanisms of neurological impact
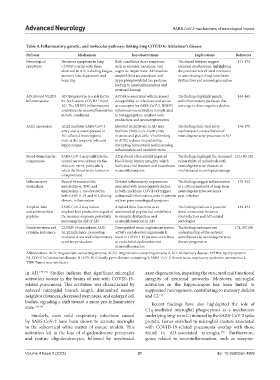
Table 4. Inflammatory, genetic, and molecular pathways linking long COVID to Alzheimer’s disease
Pathway Mechanism Key observations Implications Reference
Neurological Persistent symptoms in long Both conditions share symptoms The shared features suggest 171-173
symptoms COVID overlap with those such as anosmia, insomnia, and common mechanisms, highlighting
observed in AD, including fatigue, cognitive impairment. AD involves the potential role of viral infections
memory loss, depression, and amyloid-beta accumulation and in contributing to long-term brain
brain fog hyperphosphorylated tau proteins, dysfunction and neurodegeneration
leading to neuroinflammation and
neuronal damage
APOE4 and NLRP3 APOE4 genotype is a risk factor APOE4 is associated with increased The findings highlight genetic 163-165
inflammasome for both severe COVID-19 and susceptibility to infections and serves and inflammatory pathways that
AD. The NLRP3 inflammasome as a receptor for SARS-CoV-2. NLRP3 converge to drive cognitive decline
contributes to neuroinflammation inflammasome activation is implicated
in both conditions in tau aggregation, amyloid-beta
production, and neurodegeneration
ACE2 expression ACE2 mediates SARS-CoV-2 Elevated ACE2 levels in AD may The findings link viral entry 176-178
entry and is overexpressed in facilitate SARS-CoV-2 entry into mechanisms to exacerbation of
AD-affected brain regions, neurons and glial cells. Viral binding neurodegenerative processes in AD
such as the temporal lobe and to ACE2 reduces its availability,
hippocampus disrupting homeostasis and increasing
inflammation and oxidative stress
Blood-brain barrier SARS-CoV-2 may infiltrate the AD patients often exhibit impaired The findings highlight the increased 132,180-182
compromise central nervous system via the blood-brain barrier integrity, which vulnerability of individuals with
olfactory nerve, particularly facilitates viral invasion and exacerbates neurodegenerative diseases to
when the blood-brain barrier is neuroinflammation viral-induced neurological damage
compromised
Inflammatory Shared biomarkers like Elevated inflammatory responses are The findings suggest inflammation 139-142
biomarkers interleukin-6, TNF, and associated with neurocognitive decline as a critical mediator of long-term
interleukin-1, are elevated in in both conditions. COVID-19 triggers neurodegenerative outcomes
both COVID-19 and AD, driving widespread inflammation, even in patients post-infection
chronic inflammation. without prior neurological symptoms
Amyloid-beta SARS-CoV-2 may induce Amyloid-beta functions as an The findings indicate a potential 149-152
and antimicrobial amyloid-beta production as part of antimicrobial peptide but contributes direct connection between
peptides the immune response, potentially to synaptic dysfunction and viral infection and AD-related
increasing the risk of AD neuroinflammation in AD pathologies
Oxidative stress and COVID-19 exacerbates ACE/ Dysregulated renin-angiotensin system The findings enhances our 171,187,188
cytokine imbalance ACE2 imbalance, promoting activity and elevated angiotensin II understanding of the systemic
oxidative stress and inflammatory levels in COVID-19 patients contribute contributions to neurodegenerative
cytokine production to endothelial dysfunction and disease progression
neuroinflammation
Abbreviations: ACE: Angiotensin‑converting enzyme; ACE2: Angiotensin‑converting enzyme 2; AD: Alzheimer’s disease; APOE4: Apolipoprotein
E4; COVID: Coronavirus disease; NLRP3: NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; SARS‑CoV‑2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2;
TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
in AD. 147-152 Studies indicate that significant microglial axon degeneration, impairing the structural and functional
activation occurs in the brains of rats with COVID-19- integrity of neuronal networks. Moreover, microglial
related pneumonia. This activation was characterized by activation in the hippocampus has been linked to
reduced microglial branch length, diminished nearest suppressed neurogenesis, contributing to memory deficits
neighbor distances, decreased stem areas, and enlarged cell and CI. 155
bodies, signaling a shift toward a more pro-inflammatory Recent findings have also highlighted the role of
state. 153,154 C1q-mediated microglial phagocytosis as a mechanism
Similarly, even mild respiratory infections caused underlying long-term CI induced by the SARS-CoV-2 spike
by SARS-CoV-2 have been shown to activate microglia protein. Genes enriched in microglial clusters associated
in the subcortical white matter of mouse models. This with COVID-19-related pneumonia overlap with those
156
activation led to the loss of oligodendrocyte precursors found in AD-associated microglia. Furthermore,
and mature oligodendrocytes, followed by myelinated genes related to neuroinflammation, such as receptor-
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 21 doi: 10.36922/an.4909