Page 27 - ARNM-2-3
P. 27
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine QC parameters in radiopharmaceuticals
Table 1. (Contiuned)
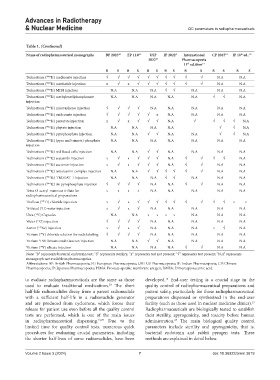
Name of radiopharmaceutical monographs BP 2023 10 EP 11.0 11 USP IP 2022 9 International CP 2015 14 JP 18 ed.. 15
th
2022 12 Pharmacopoeia
11 ed.ition 13
th
B S B S B S B S B S B S B S
Technetium ( Tc) medronate injection √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ N.A N.A
99m
99m
Technetium ( Tc) mertiatide injection x √ x √ √ √ √ √ √ √ N.A N.A
Technetium ( Tc) MIBI injection N.A N.A N.A √ √ N.A N.A N.A
99m
Technetium ( Tc) methylenediphosphonate N.A N.A N.A N.A N.A √ √ N.A
99m
injection
Technetium ( Tc) microspheres injection √ √ √ √ N.A N.A N.A N.A N.A
99m
Technetium ( Tc) oxidronate injection √ √ √ √ √ x N.A N.A N.A N.A
99m
Technetium ( Tc) pentetate injection x √ x √ √ √ N.A √ √ √ √ N.A
99m
99m
Technetium ( Tc) phytate injection N.A N.A N.A N.A √ √ N.A
Technetium ( Tc) pyrophosphate injection N.A N.A √ √ N.A N.A √ √ N.A
99m
Technetium ( Tc) (pyro and trimeta) phosphate N.A N.A N.A N.A N.A N.A N.A
99m
injection
Technetium ( Tc) red blood cells injection N.A N.A √ √ N.A N.A N.A N.A
99m
99m
Technetium ( Tc) sestamibi injection x √ x √ √ √ N.A √ √ √ √ N.A
Technetium ( Tc) succimer injection x √ x √ √ √ N.A √ √ N.A N.A
99m
Technetium ( Tc) tetrofosmin complex injection N.A N.A √ √ √ √ √ √ N.A N.A
99m
Technetium ( Tc)-TRODAT-1 Injection N.A N.A N.A √ √ N.A N.A N.A
99m
Technetium ( Tc) tin pyrophosphate injection √ √ √ √ N.A N.A √ √ N.A N.A
99m
Tetra-O-acetyl-mannose triflate for x x x x N.A N.A N.A N.A N.A
radiopharmaceutical preparations
Thallous ( TI) chloride injection x √ x √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ x x
201
3
Tritiated ( H) water injection x √ x √ N.A N.A N.A N.A N.A
Urea ( C) Capsules N.A N.A x x x x N.A N.A N.A
14
Water ( O) injection √ √ √ √ N.A N.A N.A N.A N.A
15
Xenon ( Xe) injection x √ x √ N.A N.A N.A x √ N.A
133
Yttrium ( Y) chloride solution for radiolabeling √ √ √ √ N.A N.A N.A N.A N.A
90
Yttrium Y 90 ibritumomab tiuxetan injection N.A N.A √ √ N.A N.A N.A N.A
Yttrium ( Y) silicate injection N.A N.A N.A N.A √ √ N.A N.A
90
Note: “B” represents bacterial endotoxin test; “S” represents sterility; “x” represents test not present; “√” represents test present; “N.A” represents
monograph not available in pharmacopeias.
Abbreviations: BP: British Pharmacopoeia; EP: European Pharmacopoeia; USP: US Pharmacopoeia; IP: Indian Pharmacopoeia; CP: Chinese
Pharmacopoeia; JP: Japanese Pharmacopoeia; PSMA: Prostate-specific membrane antigen; DMSA: Dimercaptosuccinic acid.
to evaluate radiopharmaceuticals are the same as those developed. End-user testing is a crucial stage in the
16
used to evaluate traditional medications. The short quality control of radiopharmaceutical preparations and
23
half-life radionuclides decay from a parent radionuclide patient safety, particularly for those radiopharmaceutical
with a sufficient half-life in a radionuclide generator preparations dispensed or synthesized in the end-user
and are produced from cyclotrons, which forces their facility (such as those used in nuclear medicine clinics).
13
release for patient use even before all the quality control Radiopharmaceuticals are biologically tested to establish
tests are performed, which is one of the main issues their sterility, apyrogenicity, and toxicity before human
in radiopharmaceutical dispensing. 13,25 Due to the administration. The main biological quality control
23
limited time for quality control tests, numerous quick parameters include sterility and apyrogenicity, that is,
procedures for evaluating crucial parameters, including bacterial endotoxin and rabbit pyrogen tests. These
the shorter half-lives of some radionuclides, have been methods are explained in detail below.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2024) 7 doi: 10.36922/arnm.3619