Page 27 - ARNM-3-2
P. 27
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Lipid-radiotherapy crosstalk in cancer
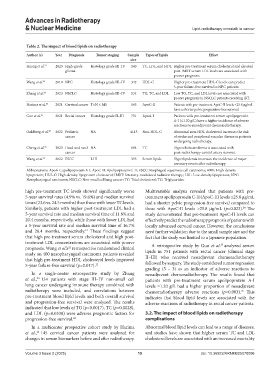
Table 2. The impact of blood lipids on radiotherapy
Author (s) Year Diagnosis Tumor staging Sample Types of lipids Effect
size
Huang et al. 21 2023 High-grade Histology grade III–IV 140 TC, LDL, and HDL Higher pre-treatment serum cholesterol and elevated
glioma post-IMRT serum LDL levels are associated with
poorer prognosis.
Wang et al. 22 2019 NPC Histology grade III–IV 342 HDL-C Higher pre-treatment HDL-C levels can predict
5-year failure-free survival in NPC patients.
Zhang et al. 23 2023 NSCLC Histology grade III–IV 134 TG, TC, and LDL Low TG, TC, and LDL levels are associated with
poorer prognosis in NSCLC patients receiving iRT.
Harima et al. 24 2021 Cervical cancer T×N × M0 145 ApoC-II Patients with pre-treatment ApoC-II levels ≤25.8 μg/mL
have a shorter pelvic progression-free survival.
Guo et al. 25 2021 Rectal cancer Histology grade II–III 751 ApoA-I Patients with pre-treatment serum apolipoprotein
A-I (≤1.20 g/L) have a higher incidence of adverse
reactions to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy.
Goldberg et al. 27 2022 Pediatric NA 4115 Non-HDL-C Abnormal non-HDL cholesterol increases the risk
cancer of stroke and peripheral vascular disease in patients
undergoing radiotherapy.
Cheng et al. 28 2023 Head-and-neck NA 694 TC Hypercholesterolemia is associated with
cancer post-radiotherapy carotid artery stenosis.
Wang et al. 29 2022 ESCC I-III 355 Serum lipids Hyperlipidemia increases the incidence of major
coronary events after radiotherapy.
Abbreviations: ApoA-I: apolipoprotein A-I; ApoC-II: Apolipoprotein C-II; ESCC: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; HDL: High-density
lipoprotein; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; IMRT: Intensity-modulated radiation therapy; LDL: Low-density lipoprotein; NPC:
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma; NSCLC: Non-small cell lung cancer; TC: Total cholesterol; TG: Triglycerides.
high pre-treatment TC levels showed significantly worse Multivariable analysis revealed that patients with pre-
5-year survival rates (4.9% vs. 19.6%) and median survival treatment apolipoprotein C-II (ApoC-II) levels ≤25.8 μg/mL
times (23.6 vs. 24.5 months) than those with lower TC levels. had a shorter pelvic progression-free survival compared to
Similarly, patients with higher post-treatment LDL had a those with ApoC-II levels >25.8 μg/mL (p=0.023). The
24
5-year survival rate and median survival time of 11.8% and study demonstrated that pre-treatment ApoC-II levels can
20.4 months, respectively, while those with lower LDL had effectively predict the radiotherapy prognosis of patients with
a 5-year survival rate and median survival time of 16.7% locally advanced cervical cancer. However, the conclusions
21
and 28.4 months, respectively. These findings suggest need further validation due to the small sample size and the
that high pre-treatment serum cholesterol and high post- fact that the study was limited to a Japanese population.
treatment LDL concentrations are associated with poorer A retrospective study by Guo et al. analyzed serum
25
prognosis. Wang et al.’s retrospective randomized clinical
22
study on 400 nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients revealed lipids in 751 patients with rectal cancer (clinical stage
that high pre-treatment HDL cholesterol levels improved II–III) who received neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
5-year failure-free survival (p=0.017). 22 followed by surgery. The study considered tumor regression
grading (5 – 3) as an indicator of adverse reactions to
In a single-center retrospective study by Zhang neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. The results found that
et al., 134 patients with stage III–IV non-small cell patients with pre-treatment serum apolipoprotein A-I
23
lung cancer undergoing immune therapy combined with levels ≤1.20 g/L had a higher proportion of neoadjuvant
radiotherapy were included, and correlations between chemoradiotherapy adverse reactions (p=0.003). This
25
pre-treatment blood lipid levels and both overall survival indicates that blood lipid levels are associated with the
and progression-free survival were analyzed. The results adverse reactions of radiotherapy in rectal cancer patients.
indicated that low levels of TG (p=0.0017), TC (p=0.0028),
and LDL (p=0.0330) were adverse prognostic factors for 3.2. The impact of blood lipids on radiotherapy
progression-free survival. 23 complications
In a multicenter prospective cohort study by Harima Abnormal blood lipid levels can lead to a range of diseases,
et al., 145 cervical cancer patients were analyzed for and studies have shown that higher serum TC and LDL
24
changes in serum biomarkers before and after radiotherapy. cholesterol levels are associated with an increased mortality
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2025) 19 doi: 10.36922/ARNM025070006