Page 75 - BH-2-2
P. 75
Brain & Heart A mini-review on heart-brain communication
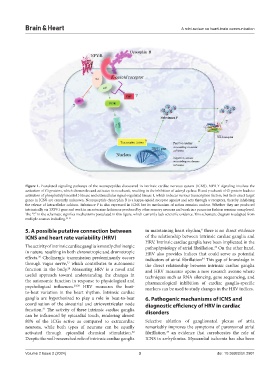
Figure 1. Postulated signaling pathways of the neuropeptides discovered in intrinsic cardiac nervous system (ICNS). NPR-Y signaling involves the
activation of Gi proteins, which dismantles and activates its α subunit, resulting in the inhibition of adenyl cyclase. Β and γ subunit of Gi protein leads to
activation of phosphatidyl inositol 3 kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1, which induces various transcription factors, but their exact target
genes in ICNS are currently unknown. Neuropeptide dynorphin B is a kappa opioid receptor agonist and acts through κ receptors, thereby inhibiting
the release of intracellular calcium. Substance P is also expressed in ICNS but its mechanism of action remains unclear. Whether they are produced
intrinsically via TRPV1 gene and work in an autocrine fashion or produced by other sensory neurons and work in a paracrine fashion remains unexplored.
The “?” in the schematic signifies mechanisms postulated in this figure, which currently lack scientific evidence. This schematic diagram is adapted from
multiple sources including. 22-25
5. A possible putative connection between in maintaining heart rhythm, there is no direct evidence
6
ICNS and heart rate variability (HRV) of the relationship between intrinsic cardiac ganglia and
HRV. Intrinsic cardiac ganglia have been implicated in the
The activity of intrinsic cardiac ganglia is mostly cholinergic pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation. On the other hand,
33
in nature, resulting in both chronotropic and dromotropic HRV also provides indices that could serve as potential
effects. Cholinergic transmission predominantly occurs indicators of atrial fibrillation This gap of knowledge in
26
34
through vagus nerve, which contributes to autonomic the direct relationship between intrinsic cardiac ganglia
27
28
function in the body. Measuring HRV is a novel and and HRV measures opens a new research avenue where
useful approach toward understanding the changes in techniques such as RNA silencing, gene sequencing, and
the autonomic function in response to physiological and pharmacological inhibition of cardiac ganglia-specific
psychological influences. 29,30 HRV measures the beat- markers can be used to study changes in the HRV indices.
to-beat variation in the heart rhythm. Intrinsic cardiac
ganglia are hypothesized to play a role in beat-to-beat 6. Pathogenic mechanisms of ICNS and
coordination of the sinoatrial and atrioventricular node diagnostic efficiency of HRV in cardiac
function. The activity of these intrinsic cardiac ganglia disorders
31
can be influenced by epicardial touch, rendering almost
80% of the ICGs active as compared to extracardiac Selective ablation of ganglionated plexus of atria
neurons, while both types of neurons can be equally remarkably improves the symptoms of paroxysmal atrial
activated through epicardial chemical stimulation. fibrillation, an evidence that corroborates the role of
35
32
Despite the well-researched role of intrinsic cardiac ganglia ICNS in arrhythmias. Myocardial ischemia has also been
Volume 2 Issue 2 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/bh.2901