Page 101 - BH-2-3
P. 101
Brain & Heart L2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria
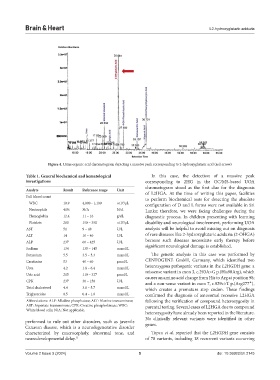
Figure 4. Urine organic acid chromatogram depicting a massive peak corresponding to 2-hydroxyglutaric acid (red arrow)
Table 1. General biochemical and hematological In this case, the detection of a massive peak
investigations corresponding to 2HG in the GC/MS-based UOA
chromatogram stood as the first clue for the diagnosis
Analyte Result Reference range Unit of L2HGA. At the time of writing this paper, facilities
Full blood count to perform biochemical tests for detecting the absolute
WBC 10.9 4,000 - 1,100 ×10 /µL configuration of D and L forms were not available in Sri
3
Neutrophils 41% N/A N/A Lanka; therefore, we were facing challenges during the
Hemoglobin 12.4 11 – 16 g/dL diagnostic process. In children presenting with learning
Platelets 260 150 – 350 ×10 /µL disability and neurological involvement, performing UOA
3
AST 51 9 – 48 U/L analysis will be helpful to avoid missing out on diagnosis
ALT 14 10 – 40 U/L of rare diseases like 2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria (2-OHGA)
ALP 237 60 – 425 U/L because such diseases necessitate early therapy before
Sodium 134 135 – 145 mmol/L significant neurological damage is established.
Potassium 5.5 3.5 – 5.3 mmol/L The genetic analysis in this case was performed by
Creatinine 53 40 – 60 µmol/L CENTOGENE GmbH, Germany, which identified two
heterozygous pathogenic variants in the L2HGDH gene: a
Urea 4.2 1.8 – 6.4 mmol/L
Uric acid 215 119 – 327 µmol/L missense variant in exon 3, c.293A>G p.(His98Arg), which
causes an amino acid change from His to Arg at position 98;
CPK 237 30 – 150 U/L and a non-sense variant in exon 7, c.829c>T p.(Arg277٭),
Total cholesterol 4.4 3.6 – 5.7 mmol/L which creates a premature stop codon. These findings
Triglycerides 0.5 0.4 – 1.8 mmol/L confirmed the diagnosis of autosomal recessive L2HGA
Abbreviations: ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; ALT: Alanine transaminase; following the verification of compound heterozygosity in
AST: Aspartate transaminase; CPK: Creatine phosphokinase; WBC: parental testing. Several cases of L2HGA due to compound
White blood cells; N/A: Not applicable.
heterozygosity have already been reported in the literature.
No clinically relevant variants were identified in other
performed to rule out other disorders, such as juvenile genes.
Canavan disease, which is a neurodegenerative disorder
characterized by macrocephaly, abnormal tone, and Topcu et al. reported that the L2HGDH gene consists
neurodevelopmental delay. 11 of 70 variants, including 18 recurrent variants occurring
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/bh.2145