Page 41 - BH-3-1
P. 41
Brain & Heart Depression, anxiety and blood pressure control
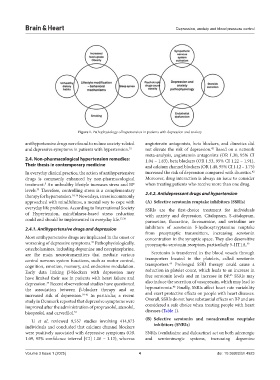
Figure 1. Pathophysiology of hypertension in patients with depression and anxiety
antihypertensive drugs were found to reduce anxiety-related angiotensin antagonists, beta blockers, and diuretics did
42
and depressive symptoms in patients with hypertension. 32 not elevate the risk of depression. Based on a network
meta-analysis, angiotensin antagonists (OR 1.30, 95% CI
2.4. Non-pharmacological hypertension remedies: 1.04 – 1.63), beta blockers (OR 1.53, 95% CI 1.22 – 1.91),
Their thesis in contemporary medicine and calcium channel blockers (OR 1.40, 95% CI 1.12 – 1.75)
42
In everyday clinical practice, the action of antihypertensive increased the risk of depression compared with diuretics.
drugs is commonly enhanced by non-pharmacological Moreover, drug interaction is always an issue to consider
3
treatment. An unhealthy lifestyle increases stress and BP when treating patients who receive more than one drug.
levels. Therefore, controlling stress is a complementary
33
therapy for hypertension. 34-36 Nowadays, stress is commonly 2.4.2. Antidepressant drugs and hypertension
approached with mindfulness, a mental way to cope with (A) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
everyday life problems. According to International Society SSRIs are the first-choice treatment for individuals
of Hypertension, mindfulness-based stress reduction with anxiety and depression. Citalopram, S-citalopram,
could and should be implemented in everyday life. 37,38 paroxetine, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, and sertraline are
2.4.1. Antihypertensive drugs and depression inhibitors of serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine reuptake
from presynaptic transmitters, increasing serotonin
Most antihypertensive drugs are implicated in the onset or concentration in the synaptic space. They also desensitize
worsening of depressive symptoms. Pathophysiologically, prosynaptic serotonin receptors, particularly 5-HT1A. 43
39
catecholamines, including dopamine and norepinephrine,
are the main neurotransmitters that mediate various Serotonin is transferred in the blood vessels through
central nervous system functions, such as motor control, transporters located in the platelets, called serotonin
44
cognition, emotion, memory, and endocrine modulation. transporters. Prolonged SSRI therapy could cause a
Early data linking β-blockers with depression may reduction in platelet count, which leads to an increase in
45
have limited their use in patients with heart failure and free serotonin levels and an increase in BP. SSRIs may
39
depression. Recent observational studies have questioned also induce the secretion of vasopressin, which may lead to
46
the association between β-blocker therapy and an hyponatremia. Finally, SSRIs affect heart rate variability
increased risk of depression. 39-41 In particular, a recent and exert protective effects on people with heart diseases.
study in Denmark reported that depressive symptoms were Overall, SSRIs do not have substantial effects on BP and are
improved after the administration of propranolol, atenolol, considered a safe choice when treating people with heart
bisoprolol, and carvedilol. 39 diseases (Table 1).
Li et al. reviewed 9,557 studies involving 414,873 (B) Selective serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake
individuals and concluded that calcium channel blockers inhibitors (SNRIs)
were positively associated with depressive symptoms (OR SNRIs (venlafaxine and duloxetine) act on both adrenergic
1.09, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.06 – 1.13), whereas and serotoninergic systems, increasing dopamine
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/bh.4923