Page 42 - BH-3-1
P. 42
Brain & Heart Depression, anxiety and blood pressure control
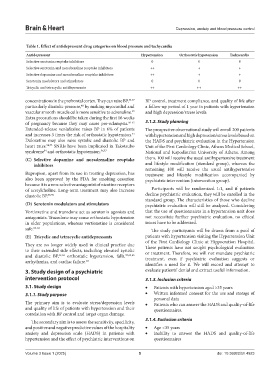
Table 1. Effect of antidepressant drug categories on blood pressure and tachycardia
Antidepressant Hypertension Orthostatic hypotension Tachycardia
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors 0 0 0
Selective serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors ++ + +
Selective dopamine and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors ++ + +
Serotonin modulators and stimulators 0 0 0
Tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants ++ ++ ++
concentrations in the prefrontal cortex. They can raise BP, 44,47 BP control, treatment compliance, and quality of life after
particularly diastolic pressure, by making myocardial and a follow-up period of 1 year in patients with hypertension
48
49
vascular smooth muscle cells more sensitive to adrenaline. and high depression/stress levels.
Extra precautions should be taken during the first 16 weeks
of pregnancy because they may cause pre-eclampsia. 50-52 3.1.2. Study planning
Extended-release venlafaxine raises BP in 6% of patients The prospective observational study will enroll 200 patients
53
and increases 3 times the risk of orthostatic hypotension. with hypertension and high depression/stress levels based on
Duloxetine may also raise systolic and diastolic BP and the HADS and psychiatric evaluation in the Hypertension
heart rates. 54,55 SNRIs have been implicated in Takotsubo Unit of the First Cardiology Clinic, Athens Medical School,
syndrome and orthostatic hypotension. 56,57 National and Kapodistrian University of Athens. Among
54
(C) Selective dopamine and noradrenaline reuptake them, 100 will receive the usual antihypertensive treatment
inhibitors and lifestyle modification (standard group), whereas the
remaining 100 will receive the usual antihypertensive
Bupropion, apart from its use in treating depression, has treatment and lifestyle modification accompanied by
also been approved by the FDA for smoking cessation psychiatric intervention (intervention group).
because it is a non-selective antagonist of nicotine receptors
of acetylcholine. Long-term treatment may also increase Participants will be randomized 1:1, and if patients
diastolic BP. 58,59 decline psychiatric evaluation, they will be enrolled in the
standard group. The characteristics of those who decline
(D) Serotonin modulators and stimulators psychiatric evaluation will still be analyzed. Considering
Vortioxetine and trazodone act as serotonin agonists and that the use of questionnaires in a hypertension unit does
antagonists. Trazodone may cause orthostatic hypotension not necessitate further psychiatric evaluation, no ethical
in older populations, whereas vortioxetine is considered issues have to be addressed.
safe. 60-62 The study participants will be drawn from a pool of
(E) Tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants patients with hypertension visiting the Hypertension Unit
of the First Cardiology Clinic at Hippocration Hospital.
They are no longer widely used in clinical practice due These patients have not sought psychological evaluation
to their extended side effects, including elevated systolic or treatment. Therefore, we will not mandate psychiatric
and diastolic BP, 44,63 orthostatic hypotension, falls, 57,64,65 treatment, even if psychiatric evaluation suggests or
arrhythmias, and cardiac failure. 66 identifies a need for it. We will record and attempt to
3. Study design of a psychiatric evaluate patients’ denial and extract useful information.
intervention protocol 3.1.3. Inclusion criteria
3.1. Study design • Patients with hypertension aged >35 years
3.1.1. Study purpose • Written informed consent for the use and storage of
personal data
The primary aim is to evaluate stress/depression levels • Patients who can answer the HADS and quality-of-life
and quality of life of patients with hypertension and their questionnaires.
correlation with BP control and target organ damage.
3.1.4. Exclusion criteria
The secondary aim is to assess the sensitivity, specificity,
and positive and negative predictive values of the hospitality • Age <35 years
anxiety and depression scale (HADS) in patients with • Inability to answer the HADS and quality-of-life
hypertension and the effect of psychiatric interventions on questionnaires
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/bh.4923