Page 79 - BH-3-3
P. 79
Brain & Heart Updates on the treatment of PFO
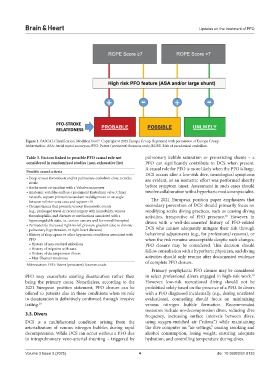
Figure 1. PASCAL Classification. Modified from . Copyright © 2025 Europa Group. Reprinted with permission of Europa Group.
8
Abbreviation: ASA: Atrial septal aneurysm; PFO: Patent (persistent) foramen ovale; ROPE: Risk of paradoxical embolism.
Table 3. Factors linked to possible PFO causal role not pulmonary bubble saturation or pre-existing shunts – a
considered in randomized studies (non‑exhaustive list) PFO can significantly contribute to DCS when present.
A causal role for PFO is more likely when the PFO is large,
Possible causal criteria DCS occurs after a low-risk dive, neurological symptoms
• Deep venous thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism close to index are evident, or an isometric effort was performed shortly
stroke
• Stroke onset co‑incident with a Valsalva maneuver before symptom onset. Assessment in such cases should
• Anatomic variables such as a prominent Eustachian valve, Chiari involve collaboration with a hyperbaric medicine specialist.
network, septum primum/secundum malalignment or an angle
between inferior vena cava and septum<10 The 2021 European position paper emphasizes that
• Circumstances that promote venous thrombotic events secondary prevention of DCS should primarily focus on
(e.g., prolonged travel or recent surgery with immobility, venous modifying scuba diving practices, such as ceasing diving
thrombophilia, and diseases or medications associated with a activities, irrespective of PFO presence. However, in
10
hypercoagulable state, i.e., certain cancers and hormonal therapies) divers with a well-documented history of PFO-related
• Permanently increased right‑to‑left pressure gradient (due to chronic
pulmonary hypertension, or right heart diseases) DCS who cannot adequately mitigate their risk through
• History of sleep apnea or other hypoxemic conditions associated with behavioral adjustments (e.g., for professional reasons), or
PFO when the risk remains unacceptable despite such changes,
• History of non‑cerebral embolism PFO closure may be considered. This decision should
• History of migraine with aura follow consultation with a hyperbaric physician, and diving
• History of decompression illness
• May‑Thurner syndrome activities should only resume after documented evidence
Abbreviation: PFO: Patent (persistent) foramen ovale. of complete PFO closure.
Primary prophylactic PFO closure may be considered
PFO may exacerbate existing desaturation rather than in select professional divers engaged in high-risk work.
10
being the primary cause. Nonetheless, according to the However, low-risk recreational diving should not be
2021 European position statement, PFO closure can be prohibited solely based on the presence of a PFO. In divers
offered to patients also in these conditions when its role with a PFO diagnosed incidentally (e.g., during unrelated
in desaturation is definitively confirmed through invasive evaluations), counseling should focus on minimizing
testing. 10 venous nitrogen bubble formation. Recommended
measures include no-decompression dives, reducing dive
3.3. Divers frequency, increasing surface intervals between dives,
DCS is a multifactorial condition arising from the using oxygen-enriched air (“nitrox”) while maintaining
arterialization of venous nitrogen bubbles during rapid the dive computer on “air settings,” ceasing smoking and
decompression. While DCS can occur without a PFO due alcohol consumption, losing weight, ensuring adequate
to intrapulmonary veno-arterial shunting – triggered by hydration, and controlling temperature during dives.
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/bh.8133