Page 84 - BH-3-3
P. 84
Brain & Heart Anteroinferior native septum TSP with ASD Device
through the device itself can be safely done; however, guidance. In the presence of an atrial septal closure device,
takes more time during TSP and also there is a risk of the typical “jump” of the entire transseptal system could not
2
complication related to device puncture. TSP in the be observed under fluoroscopic guidance. ICE monitoring
3
native septum is relatively safe and faster compared to TSP is very important to assess the areas of native septum not
through the device. In these cases, TSP should be guided covered by the atrial septal closure device. During the
with imaging such as transesophageal echocardiography procedure, understanding the LA anatomy seen on ICE in
or intracardiac echocardiography (ICE). In the presence relationship to the interatrial septum (IAS) is crucial. When
of an atrial septal closure device, the TSP site is typically the ICE probe is inside the RA, an anteriorly directed ICE
located posteroinferior to the interatrial native septum. view will show the anterior LA structures, including the
However, in cases with large devices (>26 mm), space in mitral valve and left atrial appendage (LAA). In Figure 2,
this area may be limited for TSP through native septum. the short axis view showed a very large atrial septal closure
4,5
Occasionally large ASD devices may cover the entire device (diameter 40 mm) covering almost the entire IAS.
septum and need TSP through an ASD closure device. In Figure 3 shows an ICE probe in the RA during tenting
5
this case series, we describe AF ablation in patients with an of the septal, and the needle was positioned inferior to
atrial septal closure device and the transseptal site is in the
anteroinferior and guided by ICE.
2. Case presentation
Eight AF ablation cases from seven patients
(aged 58.4 ± 8.7 years, two males) with a history of
symptomatic AF and implantation of ASD closure
devices were analyzed in this case series. The patients
were on oral anticoagulants and had discontinued taking
antiarrhythmic drugs before the procedure. All patients
had a single TSP. Five cases had paroxysmal AF and three
cases had persistent AF. All the patients underwent AF
ablations.
2.1. Preprocedural imaging
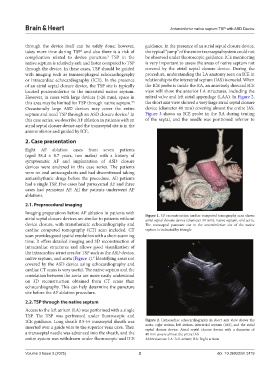
Imaging preparations before AF ablation in patients with Figure 1. 3D reconstruction cardiac computed tomography scan shows
atrial septal closure devices are similar to patients without atrial septal closure device (diameter 34 mm), native septum, and aorta.
device closure, with transthoracic echocardiography and The transseptal puncture site in the anteroinferior site of the native
cardiac computed tomography (CT) scan included. CT septum is indicated by triangle
scan provides good spatial resolution with a short scanning
time. It offers detailed imaging and 3D reconstruction of
intracardiac structures and allows good visualization of
the intracardiac structures for TSP such as the ASD device,
6
native septum, and aorta (Figure 1). Identifying areas not
covered by the ASD device using echocardiography and
cardiac CT scans is very useful. The native septum and the
correlation between the aorta are more easily understood
on 3D reconstruction obtained from CT scans than
echocardiography. This can help determine the puncture
site before the AF ablation procedure.
2.2. TSP through the native septum
Access to the left atrium (LA) was performed with a single
TSP. The TSP was performed under fluoroscopic and
ICE guidance. Long sheath 8.5-Fr transseptal sheath was Figure 2. Intracardiac echocardiography in short axis view shows the
inserted over a guide wire to the superior vena cava. Then aorta, right atrium, left atrium, interatrial septum (IAS), and the atrial
septal closure device. Atrial septal closure device with a diameter of
a transseptal needle was advanced into the sheath, and the 40 mm covers almost the entire IAS
entire system was withdrawn under fluoroscopic and ICE Abbreviations: LA: Left atrium; RA: Right atrium
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2025) 2 doi: 10.36922/bh.5119