Page 85 - BH-3-3
P. 85
Brain & Heart Anteroinferior native septum TSP with ASD Device
the device, but still above the RA floor. In our cases, we wall, with saline irrigation speed of 15 mL/min. The ablation
performed TSP to the anteroinferior area (Figure 4). lesions had an interlesion distance of ≤5 mm. The ablation
strategy in these cases primarily focused on achieving
2.3. Catheter ablations pulmonary vein isolation to establish a bidirectional block.
All AF catheter ablations were performed with patients After successful ablation, there were 3 months of blanking
under conscious sedation conducted with continuous period, and 24-hour Holter monitoring was scheduled for
intravenous infusion of fentanyl and midazolam follow-up at 3, 6, and 12 months.
Throughout the ablation procedure, the activated clotting
time was maintained within the range of 300 – 350 s. 2.4. Results
Biosense Webster Thermocool Smarttouch SF catheter Baseline characteristics of the patients are presented
ablation was employed, aiming to achieve an ablation index in Table 1. All the patients had a history of atrial septal
value of ≥450 for the anterior wall and ≥350 for the posterior closure device implantation, and the mean diameter of
the closure device was 23.8 ± 10.8 mm (10 – 40 mm).
Three-dimensional cardiac CT scan revealed adequate
space of native septum around the device, especially in the
anteroinferior area. The TSP procedures were performed
in the native septum in the anteroinferior sites of the IAS,
and the mean procedure time of TSP was 6.3 ± 2.6 min. The
success rate was 100%, and there were no complications
related to TSP. In five of the eight patients, the diameter of
the atrial septal occluders used was greater than or equal to
26 mm, with the largest device size being 40 mm. Despite
the larger size of the occluders used, left atrial access
during TSP through the native septum was still possible.
After follow-up of 7.3 ± 6.6 months (3 – 22 months), four
patients (50%) had recurrent AF after ablation.
Figure 3. Intracardiac echocardiography during transseptal puncture 3. Discussion
(TSP). TSP through native septum. Tenting of the native septum (the
star) during TSP. The needle was positioned inferior to the device (arrow). ASD is a common congenital heart disease diagnosed in
Atrial septal closure device with a diameter of 40 mm. The arrow indicates adulthood, and AF is the most common arrhythmia after
the atrial septal closure device, while the star indicates the native septum transcatheter ASD closure. AF ablation in the settings
7
Abbreviations: LA: Left atrium; RA: Right atrium of ASD closure devices is feasible and safe. However,
4,8
technical challenges may be encountered during TSP and
AF ablation for patients receiving atrial septal closure
devices, especially when a large device (>26 mm) is
involved, limiting the space at this site for TSP through
native septum. TSP can be performed through the
4,5
closure device or through areas of the native septum
not covered by the device. In our strategy for creating
LA access in the presence of atrial septal closure device,
we aimed to avoid puncturing the device, because it will
increase the difficulty of sheath and catheter manipulation,
such as rotating, withdrawing, or advancing the catheter.
TSP through the device can lead to longer transseptal
procedures, both first and second transseptal, and longer
total fluoroscopy and procedure time compared to
puncture to the native septum. Puncture through a device
9
needs more wire exchange, and some cases may need
10
a balloon to dilate the puncture site. In addition, there
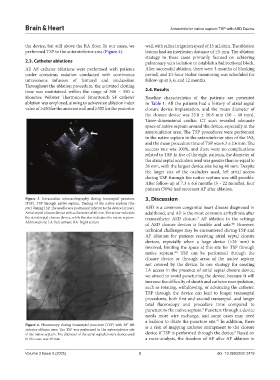
Figure 4. Fluoroscopy during transseptal puncture (TSP) with 30° left is a risk of mapping catheter entrapment to the closure
anterior oblique view. The TSP was performed in the anteroinferior site 3
of the native septum. The diameter of the atrial septal closure device used device if TSP is performed through the device. Based on
in this case was 40 mm a meta-analysis, the freedom of AF after AF ablation in
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/bh.5119