Page 139 - EER-2-2
P. 139
Explora: Environment
and Resource Tourism resources of Xinjiang
Table 2. The number and proportion of tourism destinations 4. Suggestions on tourism development in
in each heatwave index level in Xinjiang, China Xinjiang
Heatwave index level Number of destinations Ratio (%) 4.1. The development of mountain and forest
The lowest 9 1.86 tourism
Lower 23 4.75 Xinjiang’s mountain and forest tourism is highly distinctive.
Low 62 12.81 However, most existing destinations are located at lower
Medium 108 22.31 altitudes, with over 60% of them being below 1,500 m. There
High 90 18.60 is significant potential to develop higher-altitude mountain
Higher 76 15.70 and forest tourism, particularly in regions where the heat
The highest 116 23.97 levels are relatively lower, providing more comfortable
experiences. After years of development, Xinjiang’s forest
tourism has created various types of forest landscapes rich in
historical relics, cultural sights, and ethnic customs, offering
unique ecological tourism routes. The development model
has shifted from passive protection and single-use of forest
18
resources to a sustainable development pattern. According
to the estimation by Xiong and Qin, the direct economic
22
value of Xinjiang’s forests is 920 billion RMB yuan, with the
recreational value accounting for 68% of the whole direct
value. Leveraging the newly developed transportation
networks to promote forest tourism further is a key strategy
for advancing Xinjiang’s forestry tourism economy.
4.2. The development of the international market,
especially the European market
At present, international tourism revenue in Xinjiang is very
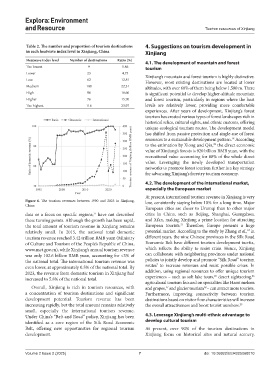
Figure 6. The tourism revenues between 1990 and 2023 in Xinjiang, low, consistently staying below 10% for a long time. Major
China
European cities are closer to Urumqi than to other major
data or a focus on specific regions, have not described cities in China, such as Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou,
21
these turning points. Although the growth has been rapid, and Xi’an, making Xinjiang a prime location for attracting
23
the total amount of tourism revenue in Xinjiang remains European tourists. Therefore, Europe presents a huge
24
relatively small. In 2015, the national total domestic potential market. According to the study by Zhang et al., in
tourism revenue reached 3.42 trillion RMB yuan (Ministry different years, the nine Chinese provinces in the Silk Road
of Culture and Tourism of the People’s Republic of China, Economic Belt have different tourism development inertia,
www.mct.gov.cn), while Xinjiang’s annual tourism revenue which reflects the ability to resist crisis. Hence, Xinjiang
was only 102.6 billion RMB yuan, accounting for <3% of can collaborate with neighboring provinces under national
the national total. The international tourism revenue was policies to jointly develop and promote “Silk Road” tourism
7
even lower, at approximately 0.5% of the national total. By routes to increase revenues and resist possible crises. In
2023, the revenue from domestic tourism in Xinjiang had addition, using regional resources to offer unique tourism
25
26
increased to 5.8% of the national total. experiences – such as salt lake tours, desert sightseeing,
agricultural tourism focused on specialties like Hami melons
Overall, Xinjiang is rich in tourism resources, with and grapes, and glacier tourism – can attract more tourists.
27
28
a concentration of tourism destinations and significant Furthermore, improving connectivity between tourism
development potential. Tourism revenue has been destinations based on visitor flow characteristics will increase
increasing rapidly, but the total amount remains relatively the overall attractiveness and boost tourist numbers. 29
small, especially the international tourism revenue.
Under China’s “Belt and Road” policy, Xinjiang has been 4.3. Leverage Xinjiang’s multi-ethnic advantage to
identified as a core region of the Silk Road Economic develop cultural tourism
Belt, offering new opportunities for regional tourism At present, over 90% of the tourism destinations in
development. Xinjiang focus on historical sites and natural scenery,
Volume 2 Issue 2 (2025) 7 doi: 10.36922/EER025060010