Page 211 - GHES-3-1
P. 211
Global Health Economics and
Sustainability
Cervical cancer screening in Maroua
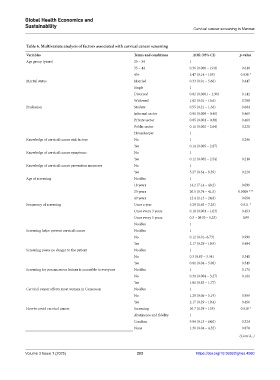
Table 6. Multivariate analysis of factors associated with cervical cancer screening
Variables Terms and conditions AOR (95% CI) p‑value
Age group (years) 25 – 34 1
35 – 44 0.36 (0.006 – 19.8) 0.610
45+ 3.47 (0.14 – 155) 0.036 *
Marital status Married 0.33 (0.01 – 5.66) 0.447
Single 1
Divorced 0.02 (0.0001 – 2.96) 0.142
Widowed 1.82 (0.01 – 15.6) 0.788
Profession Student 0.55 (0.21 – 1.36) 0.604
Informal sector 0.01 (0.009 – 0.45) 0.465
Private sector 0.05 (0.001 – 0.30) 0.469
Public sector 0.11 (0.002 – 2.64) 0.220
Housekeeper 1
Knowledge of cervical cancer risk factors No 1 0.206
Yes 0.14 (0.005 – 2.87)
Knowledge of cervical cancer symptoms No 1
Yes 0.12 (0.002 – 2.54) 0.218
Knowledge of cervical cancer prevention measures No 1
Yes 5.27 (0.34 – 8.59) 0.220
Age of screening No idea 1
18 years 14.2 (7.14 – 48.2) 0.099
25 years 20.5 (5.74 – 41.5) 0.0005 ***
40 years 12.4 (1.13 – 24.8) 0.058
Frequency of screening Once a year 3.29 (1.62 – 7.25) 0.011 *
Once every 3 years 0.18 (0.001 – 1.03) 0.453
Once every 5 years 0.3 – 08 (0 – 5.23) 0.99
No idea 1
Screening helps prevent cervical cancer No idea 1
No 0.12 (0.01−6.73) 0.999
Yes 2.17 (0.29 – 19.9) 0.494
Screening poses no danger to the patient No idea 1
No 0.3 (0.03 – 3.34) 0.340
Yes 0.01 (0.04 – 5.08) 0.349
Screening for precancerous lesions is accessible to everyone No idea 1 0.171
No 0.34 (0.004 – 3.27) 0.181
Yes 1.81 (0.83 – 1.77)
Cervical cancer affects most women in Cameroon No idea 1
No 1.29 (0.06 – 5.19) 0.959
Yes 2.17 (0.29 – 19.4) 0.456
How to avoid cervical cancer Screening 10.7 (1.39 – 135) 0.018 *
Abstinence and fidelity 1
Condom 9.04 (0.13 – 64.0) 0.324
None 1.30 (0.04 – 4.55) 0.878
(Cont'd...)
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 203 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.4080