Page 48 - GHES-3-1
P. 48
Global Health Economics and
Sustainability
COVID-19 changed our world
A
B
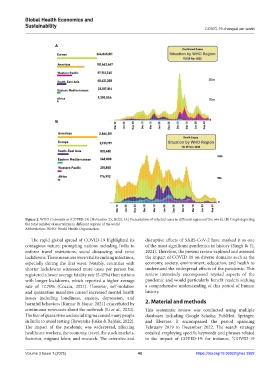
Figure 2. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) (November 25, 2022). (A) Presentation of infected cases in different regions of the world. (B) Graph depicting
the total number of mortalities in different regions of the world
Abbreviation: WHO: World Health Organization.
The rapid global spread of COVID-19 highlighted its disruptive effects of SARS-CoV-2 have marked it as one
contagious nature, prompting nations including India to of the most significant pandemics in history (Singh & Yi,
enforce travel restrictions, social distancing, and strict 2021). Therefore, the present review explored and assessed
lockdowns. These measures were vital to curbing infections, the impact of COVID-19 on diverse domains such as the
especially during the first wave. Notably, countries with economy, society, environment, education, and health to
shorter lockdowns witnessed more cases per person but understand the widespread effects of the pandemic. This
registered a lower average fatality rate (5.45%) than nations review intensively encompassed myriad aspects of the
with longer lockdowns, which reported a higher average pandemic and would particularly benefit readers seeking
rate of 12.70% (Coccia, 2021). However, self-isolation a comprehensive understanding of this period of human
and quarantine mandates caused increased mental health history.
issues including loneliness, anxiety, depression, and
harmful behaviors (Kumar & Nayar, 2021) exacerbated by 2. Material and methods
continuous newscasts about the outbreak (Li et al., 2020). This systematic review was conducted using multiple
The fear of quarantine and social stigma caused many people databases including Google Scholar, PubMed, Springer,
in India to avoid testing (Rewerska-Juśko & Rejdak, 2022). and Elsevier. It encompassed the period spanning
The impact of the pandemic was widespread, affecting February 2019 to December 2022. The search strategy
healthcare workers, the economy, travel, the stock markets, entailed employing specific keywords and phrases related
factories, migrant labor, and research. The extensive and to the impact of COVID-19: for instance, “COVID-19
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 40 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.3992